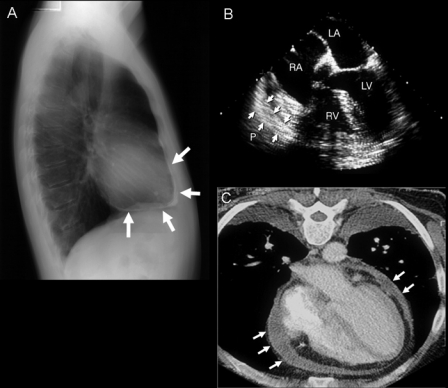
FIGURE 14.
Chest radiograph, transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), and cardiac computed tomogram typical of constrictive pericarditis. A, Pericardial calcification (arrows) on chest radiography is best seen from the lateral view over the right ventricle (RV) and across the diaphragmatic surface of the heart. Pericardial calcification reflects chronicity of constrictive pericarditis and is associated with a higher surgical mortality. B, Thickness of the pericardium is often difficult to determine by transthoracic echocardiography, but TEE is usually reliable in measuring the pericardial thickness (arrows). C, Increased pericardial thickness (arrows) can be visualized on computed tomogram of the same patient. LA = left atrium; LV = left ventricle; RA = right atrium.
Adapted from reference 63.