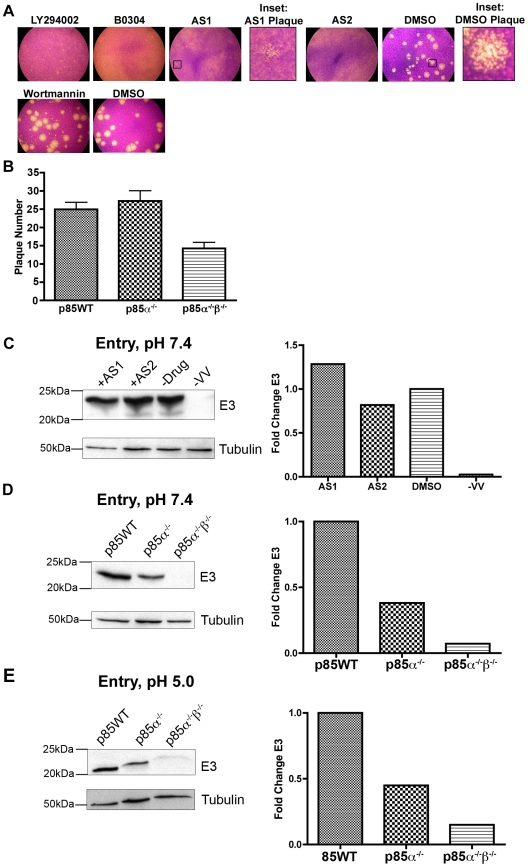
Figure 1. PI3Ks regulate plaque morphology and early protein production.
A. PI3K inhibitors reduce plaque size in BSC40 cells. Cells were infected with 100 PFU of vaccinia virus (VV), strain WR. Inhibitors were added one hour post viral entry. First row: LY294002, 20 µM; B0304, 20 µM; AS1, 50 µM; AS2, 50 µM (LY294002 and B0304 are in 0.2% DMSO and AS1 and AS2 are in 0.5% DMSO); 0.5% DMSO alone. Insets show representative plaques from 50 µM AS1 and 0.5% DMSO treated wells. Second row: 10 µM Wortmannin in 0.1% DMSO did not appear to reduce VV plaque size; 0.1% DMSO control. Results are from three independent trials. B. p85WT and p85α−/− cells form two times more plaques than p85α−/−β−/− cells. Cells were infected with equal amounts of virus and monolayers were stained with crystal violet 48 hours post infection. Results are from eight independent trials. C. PI3K inhibitors do not decrease early viral protein expression. BSC40 cells were infected at pH 7.4 and MOI = 5 with VV and PI3K inhibitors were added 1 hour post-viral entry and allowed to infect for an additional 2 hours. Proteins were subjected to western analysis by anti-E3 mAb and anti-Tubulin mAb. For quantification (right) bands were normalized to tubulin loading control and data is expressed as the fold change relative to DMSO-treated samples. D. Early protein expression is reduced in p85-deficient cells. Cells were infected at an MOI = 5 with VV at pH = 7.4 and analyzed as in C. E. Early protein expression is reduced in p85-deficient cells. Cells were infected at an MOI = 5 with VV. Virus was bound to cells at 4°C, after which cells were moved to 37°C with PBS, pH = 5. Following a 2 hour infection, equal amounts of protein were subjected to western analysis with anti-E3 mAb or anti-Tubulin, and quantitated as in C.