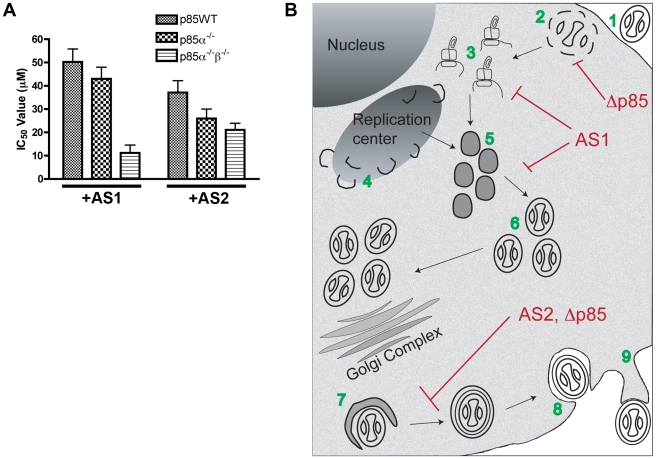
Figure 11. PI3K usage by VV is functionally redundant.
A. PI3K inhibitors reduce plaque numbers in p85-deficient cells. Drugs were added to p85-deficient cells post viral adsorption at different concentrations. The concentration of drug needed to reduce plaque numbers by half (IC50) was calculated by fitting the data to a linear regression model using Prism software (GraphPad Prism Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA). IC50 values are lower for p85-deficient cells. Results are from three independent trials. B. Summary of vaccinia virus morphogenesis in p85-deficient cells or following PI3K inhibitor treatment. After VV entry (1) virion uncoating and early protein synthesis occurs (2). These steps are followed by late protein production (3), formation of viral replication centers and viral crescents (4). Crescents envelope viroplasm to form immature virions (IV, 5). The cores of IV condense to form mature virions (IMV, 6). A subset of the IMV traffic to the Golgi Complex where they are enveloped in a host cell derived membrane to form IEV (7). IEV fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing virus to the extracellular milieu, (CEV, 8). CEV form actin tails beneath the virus and ultimately, release to form extracellular enveloped virions (EEV, 9). Our results suggest that involvement of PI3Ks at steps 2,3,5, and 7. Steps 2 and 7 are disrupted in the p85-deficient cells, AS1 treatment disrupts steps 3 and 5, and AS2 disrupts steps 7. Thus, PI3K usage by VV is redundant; multiple PI3Ks acting at each of several steps regulate VV morphogenesis.