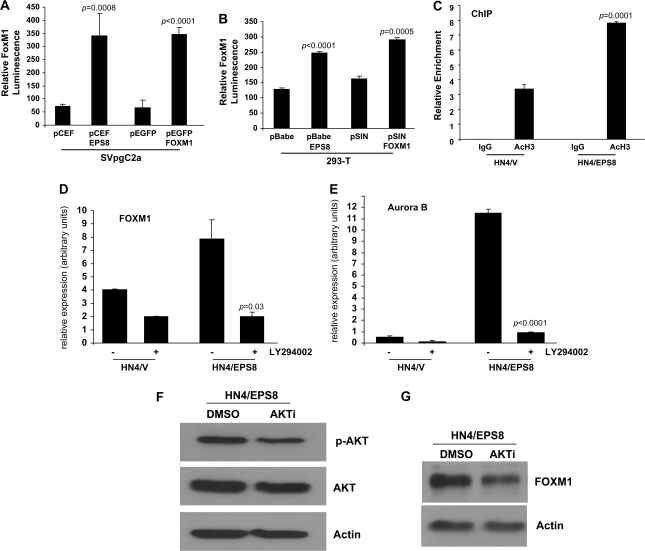
Fig. 3.
EPS8 induces FOXM1 expression via PI3K and AKT. SVpgC2a cells (A) or 293-T cells (B) were transiently transfected with the plasmids indicated, together with FOXM1B-luciferase promoter and β-galactosidase plasmids. Forty-eight hours later, luciferase assays were performed as described in Methods. FOXM1B luminescence is shown, normalized to β-galactosidase. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was performed using antibody that recognizes acetylated histone H3, or IgG as control, as described in Methods. Quantitative PCR was carried out using three sets of primers specific for the FOXM1 promoter. Data are shown for one primer set and are representative of data obtained with the other primers. (D and E) HN4/V and HN4/EPS8 cells were cultured in the presence of LY294002 (10 μM) or an equivalent volume of solvent (dimethyl sulfoxide). Twenty-four hours later, total RNA was prepared, reverse transcribed and used as template for qRT–PCR experiments using primers for FOXM1 (D) and Aurora-B kinase (E). (F and G) HN4/EPS8 cells were incubated in the presence of AKT inhibitor (AKTi) or solvent. Twenty-four hours later, cell lysates were prepared and western blotted with (F) p-AKT or (G) FOXM1 antibodies.