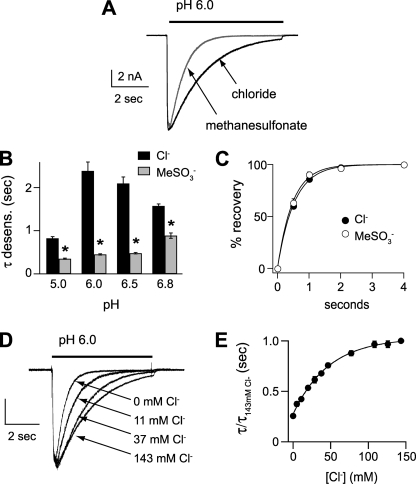
FIGURE 2.
Extracellular Cl− dose-dependently modulates the desensitization kinetics of ASIC1a. A, superimposed pH 6-evoked currents in Cl− or MeSO3− solutions. B, mean time constants of desensitization (τ) as measured from single exponential fits to the falling phase of the currents evoked by the indicated pH solutions containing high or 0 mm Cl−. (*, p < 0.01 versus currents evoked in Cl−; n ≥ 10.) C, recovery from desensitization in Cl− or MeSO3− solutions. Current was completely desensitized with a 7-s pulse to pH 6. Cells were then exposed to pH 8 solution for the indicated times before they were stimulated again with pH 6. Recovery is percentage of current evoked by the second pH 6 pulse compared with the first. To compensate for tachyphylaxis, data were normalized to currents recorded at 4 s of recovery. Lines are fits of single exponentials (n ≥ 6). D, superimposed and normalized currents evoked by pH 6 solutions containing varying mixtures of Cl−/MeSO3− solutions, demonstrating the effect of Cl− concentration on the desensitization rate. Vertical scale bar shows the following: 1 nA for 143 mm Cl−, 0.6 nA for 37 mm Cl−, and 0.5 nA for 11 mm and 0 mm Cl−. E, mean time constants of desensitization of currents recorded in solutions of varying Cl− concentration as in D, normalized to the time constant of desensitization of current recorded in 143 mm Cl− (n ≥ 4). Line is fit of the Hill equation.