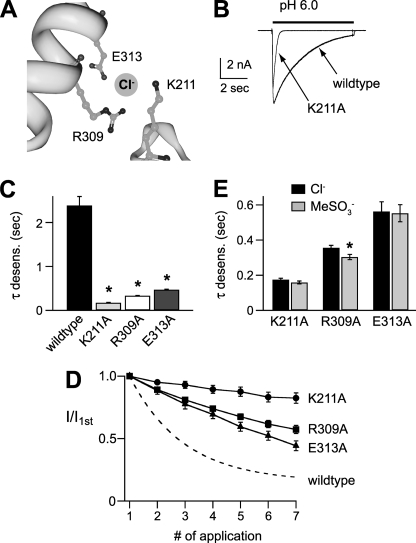
FIGURE 5.
Residues in the extracellular domain are necessary for Cl− modulation of mASIC1a. A, Cl−-binding site in chicken ASIC1a (Protein Data Bank code 2QTS) crystal structure. The site is coordinated by Arg-309 and Glu-313 from helix 4 of one subunit, and Lys-211 from an adjacent subunit. Residues are numbered per the mouse ASIC1a sequence. Image was created using the RCSB-Protein Workshop Viewer at the RCSB Protein Data Bank website. B, superimposed currents evoked by pH 6 in cells expressing wild type ASIC1a or mutant ASIC1aK211A. C, mean time constants of desensitization of pH 6-evoked currents recorded in cells expressing wild type or indicated ASIC1a mutants (n ≥ 8; *, p < 0.01 versus wild type). D, tachyphylaxis of successive pH 5-evoked current amplitudes normalized to the first pH 5 current amplitude recorded in cells expressing the indicated ASIC1a mutant (n ≥ 6). Dashed line is fit of data from Fig. 3B for wild type ASIC1a. E, mean time constants of desensitization of pH 6-evoked currents recorded in cells expressing the indicated ASIC1a mutant in either Cl− or MeSO3− solutions (n ≥ 4; *, p < 0.01 versus Cl−). Cl− data are the same as in C.