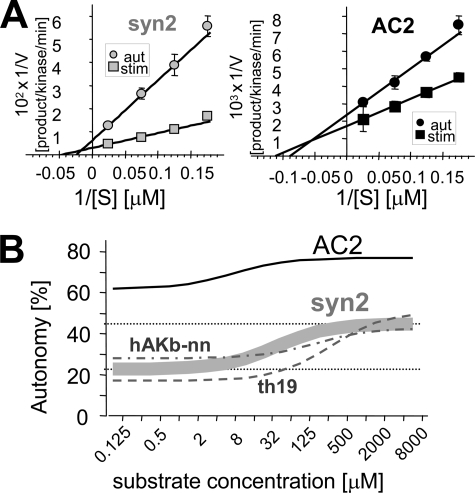
FIGURE 5.
Autonomous CaMKII activity has both decreased Vmax and increased Km compared with stimulated activity. A, double reciprocal plot of phosphorylation rate as function of substrate concentration for stimulated and autonomous CaMKII activity, for syntide2 (left) and AC2 (right). B, the difference in Km makes CaMKII autonomy additionally substrate concentration-dependent. The difference in Vmax makes autonomous activity toward syntide2 more than 2-fold further stimulated by Ca2+/CaM even at infinite substrate concentration. The curve for syntide2 is based on four independent experiments as in A (see supplemental Table S2). Two additional regular substrates, derived from human AKAP79 (hAKb-nn) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH19), respectively, (see supplemental Fig. S4) behaved very similarly as syntide2.