Fig. 1.
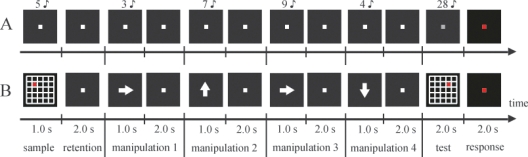
Schematic illustrations of one trial sequence for the auditory (A) and visual (B) working memory (WM) tasks. (A) In the auditory WM task, participants performed a mental calculation for numbers auditorily presented through headphones; the calculation process was repeated four times. (B) In the visual WM task, participants had to memorize the red circle’s position in the sample display and move the circle in their minds, as visually indicated by arrows; they had to perform this sequence of actions four times.
