Figure 1. Interaction and colocalization of UVRAG with C-Vps.
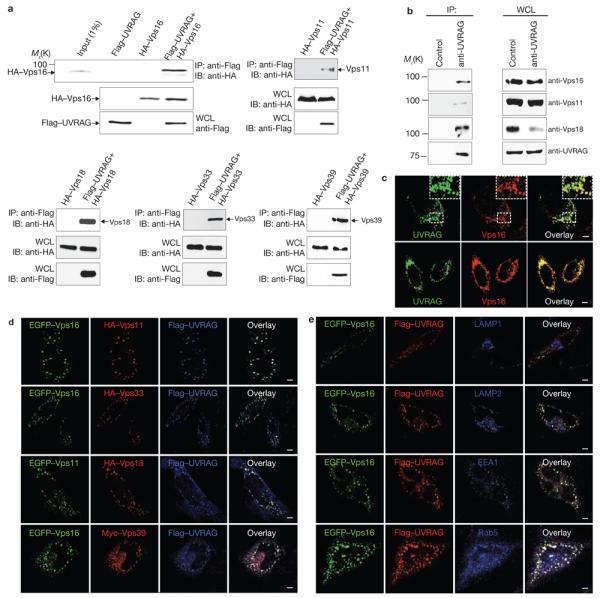
(a) UVRAG interaction with C-Vps. 293T cells were co-transfected with Flag–UVRAG and HA–Vps16, HA–Vps11, HA–Vps18, HA–Vps33 or HA–Vps39. Whole-cell lysates (WCLs) were used for immunoprecipitation (IP) with an anti-Flag antibody, followed by immunoblotting (IB) with an anti-HA antibody. 1% WCL was used as the input. (b) Interaction between endogenous UVRAG and C-Vps subunits. WCLs of 293T cells were used for IP with control serum (control) or an anti-UVRAG antibody, followed by IB with the indicated antibodies. The right panel shows endogenous protein expression. (c) Confocal microscopy analysis of the colocalization of endogenous UVRAG and Vps16 or Vps18 in HeLa cells. Insets highlight colocalization. (d) Confocal microscopy analysis of the colocalization of UVRAG with C-Vps subunits in HeLa cells transfected with Flag–UVRAG, and epitope-tagged C-Vps subunits as indicated. (e) Colocalization of UVRAG–C-Vps in early endosomes. HeLa cells were co-transfected with EGFP–Vps16 and Flag–UVRAG, stained with antibodies to LAMP1, LAMP2, EEA1 and Rab5, followed by confocal microscopy. All images are representative of at least three independent experiments. Scale bars, 5 μm. The raw data for a and b are shown in Supplementary Information, Fig. S6
