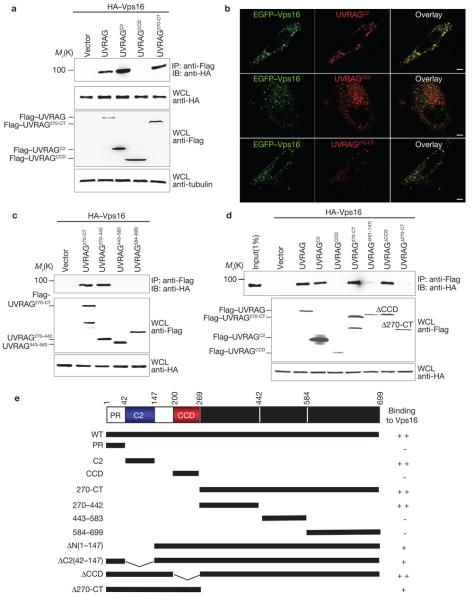
Figure 2. Mapping of Vps16 binding domains of UVRAG.
(a) The N-terminal C2 domain or the C-terminal region of UVRAG interacts individually with Vps16. 293T cells were co-transfected with HA–Vps16, together with vector, Flag–UVRAG or Flag–UVRAG mutants. WCLs were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag followed by immunoblotting with an anti-HA antibody. (b) HeLa cells were transfected with EGFP–Vps16 together with Flag–UVRAG mutants as indicated and stained with anti-Flag (red), followed by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 5 μm. (c) Interactions of the UVRAG C-terminal truncated mutants with Vps16. At 48 h post-transfection with HA–Vps16 and Flag–UVRAG C-terminal mutants, 293T WCLs were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag, followed by immunoblotting with anti-HA. (d) UVRAG C2 domain or C-terminal region deletion abolishes Vps16 binding. At 48 h post-transfection with HA–Vps16 together with Flag–UVRAG or its mutants, 293T WCLs were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag followed by immunoblotting with an anti-HA antibody. (e) Schematic representation of UVRAG and its deletion mutants. ++, strong binding; +, weak binding; −, no binding. The raw data for a, c and d are shown in Supplementary Information, Fig. S6