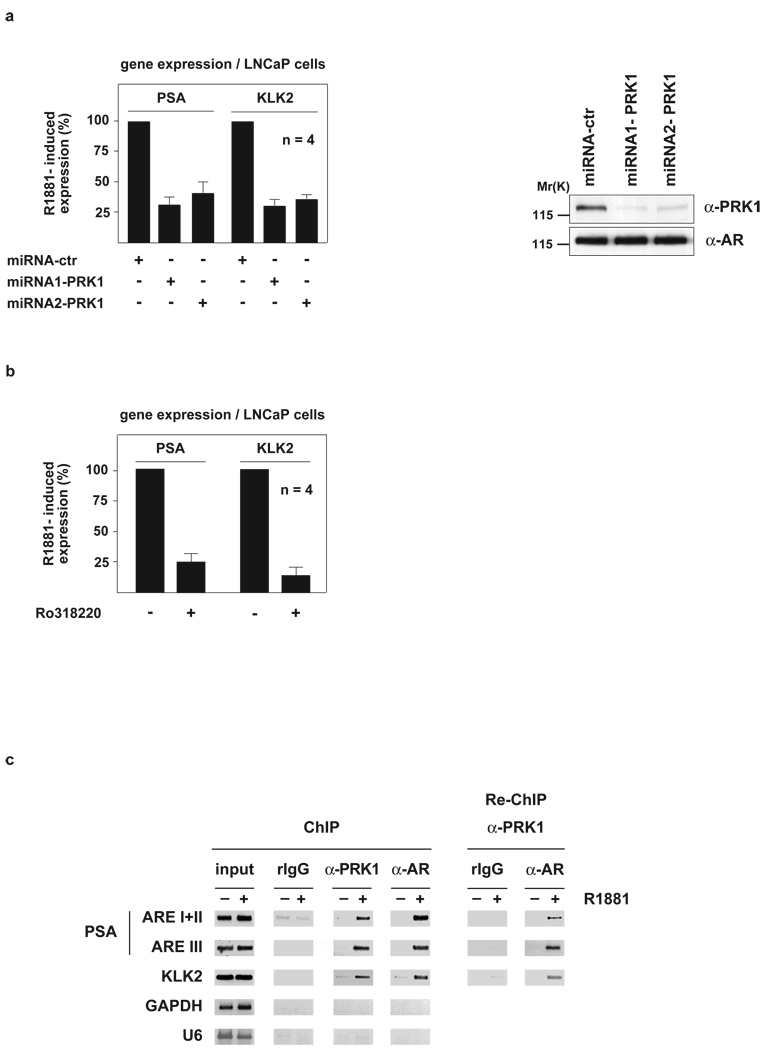
Figure 1.
PRK1 controls AR-dependent gene expression and associates with chromatin. LNCaP cells were cultivated in the presence or absence of the AR agonist R1881. miRNA-mediated PRK1 knockdown (a) or the PRK1 inhibitor Ro318220 (b) reduce expression of the endogenous PSA and KLK2 genes (a, left panel, b). Western blot analysis (a, right panel) verified the specific miRNA-mediated knockdown of PRK1. Bars represent mean +SD (n=4). ChIP and Re-ChIP (c) using the indicated antibodies demonstrate androgen-dependent association of AR and PRK1 at promoters of AR-regulated genes. The precipitated chromatin was amplified by PCR using primers flanking the AREs in the promoter region of the PSA and KLK2 genes, or the promoters of the unrelated GAPDH and U6 genes.