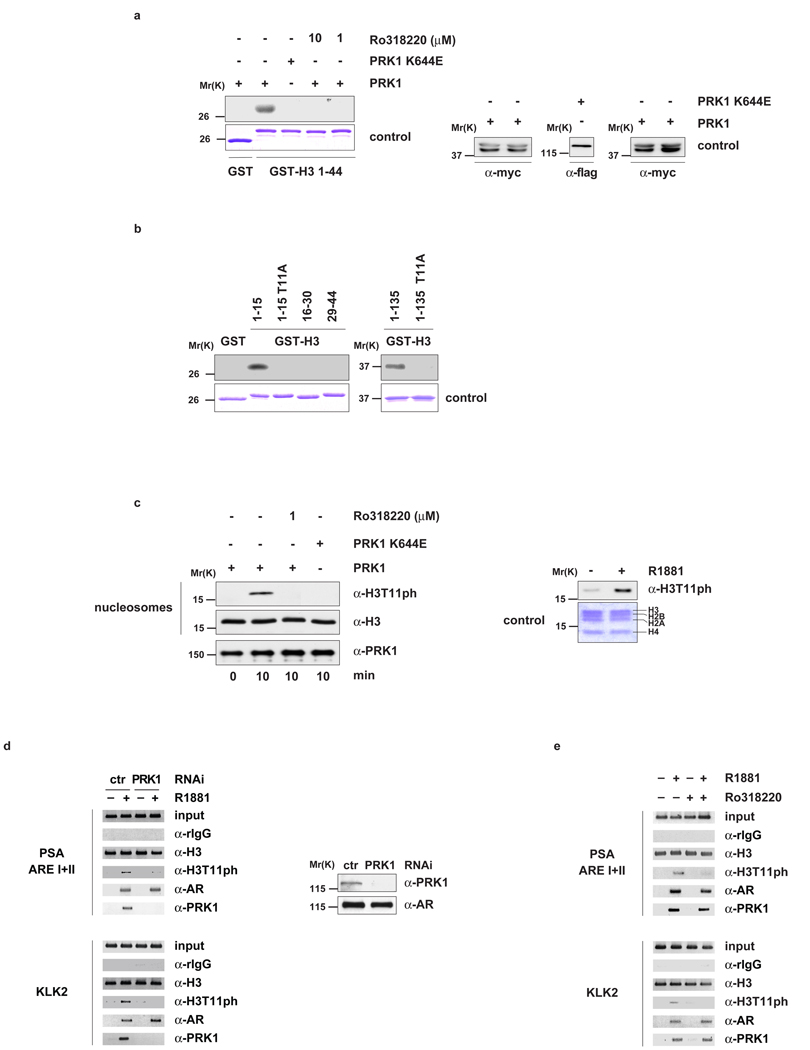
Figure 2.
PRK1 phosphorylates histone H3 at threonine 11 (H3T11). Bacterially expressed GST and GST-H3 (a, b) or nucleosomes from HeLa cells (c, left panel) were incubated for the indicated time with active PRK1 or the kinase dead mutant PRK1 K644E in the presence or absence of the inhibitor Ro318220. Coomassie blue staining (a and b, lower panels) and Western blot analyses (a, right panel) show the amounts of GST fusion proteins and PRK1 used. Western blots were decorated with the indicated antibodies (c, left panel). Nucleosomes purified from LNCaP cells cultivated in the presence or absence of R1881 for 30 minutes were analysed in Western blot (c, right panel). For ChIP (d, e), LNCaP cells were cultivated in the presence or absence of the AR agonist R1881, transfected with either siRNA (d) or treated with or without Ro318220 (e) as indicated, and subjected to ChIP with the indicated antibodies. The precipitated chromatin was amplified by PCR using primers flanking AREs in the promoter region of the PSA and KLK2 genes. Western blot analysis (d, right panel) verified the specific siRNA-mediated knockdown of PRK1.