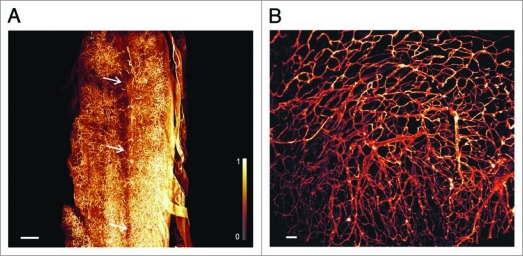
Figure 3.
3D-reconstruction of vascularization in spinal cord, and cardiac auricles. (A) Microvasculature of mouse spinal cord. Some of the thin capillaries supporting the spinal nerves are apparent. The spinal canal (Canalis spinalis) is clearly defined by its complete lack of vessels. Its position is indicated by the three arrows. (Olympus objective XLFluar 4×, N.A. 0.28, reconstructed from 610 images, 2,048 × 2,048 pixel). Image stack was deconvolved with Huygens (SVI, Hilversum, Netherlands) using a measured point spread function. Scale bar 400 µ m. (B) Reconstruction of the microvascular architecture in the cardiac auricle (Auricula atrii). (Olympus objective UPlanFL N 10×, N.A. 0.3, reconstructed from 199 images, 2,048 × 2,048 pixel), scale bar 50 µm. Monochrome images were transposed into false colors using the color map shown at the left side of (A).