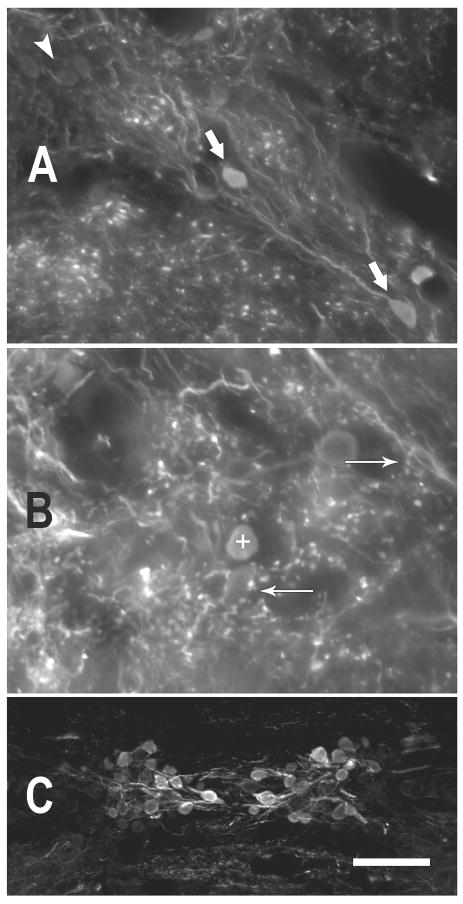
Figure 4.
Photomicrographs illustrating GABA immunoreactivity in the toadfish. A. GABA immunoreactive somata and processes in dorsal DON. GABA-negative somata (white arrowhead, upper left) are lightly visible due to autofluorescence, but were clearly differentiated from the GABA-immunoreactive somata (large white arrows). (coronal, 50 μm section) B. GABA-positive puncta surround GABA-negative somata (e.g., arrow pointing left) and are present in the neuropil of the DON. Sometimes the puncta occur in sprays (arrow pointing right) that appeared to bear multiple boutons from the same process. The + symbol marks a GABA-positive soma (dorsal DON, coronal, 25 μm section). C. The rostral efferent nucleus of cranial VIII illustrates a range of immunoreactivity among those somata. (25 μm horizontal section) More heavily GABA-IR somata are more medial (near the midline of the section). (scale bar in C = 25 μm for A,B and 100μm for C)