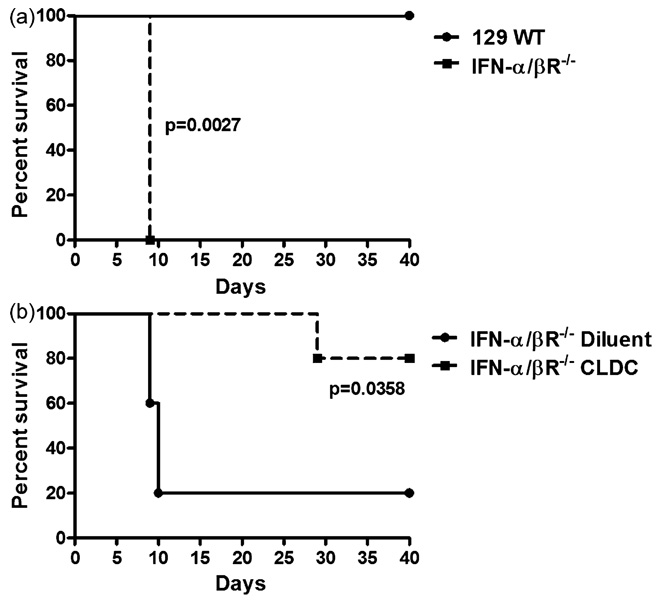
Fig. 6.
Type I interferons provide partial protection from F. tularensis LVS challenge but are not required for CLDC-induced protection. Wild-type 129 mice (n = 5 per group) and IFN-α/β receptor−/− mice on the 129 background were challenged with 105 CFU F. tularensis LVS, as noted in Section 2. In (a), mice lacking IFN-α/βR expression were all euthanized on day 9 while wild-type 129 mice were completely resistant to death from F. tularensis challenge. Kaplan-Meier survival curve differences assessed by log-rank analysis demonstrated a significant increase in survival time (p = 0.0027) in wild-type mice compared to IFN-α/βR−/− mice. Similar results were found in one additional experiment. In (b), i.n. administration of CLDC to IFN-α/βR−/− mice 24 h prior to challenge resulted in a significant increase in survival time (p = 0.0358) compared to sham-treated IFN-α/βR−/− mice. These results are representative of two independent experiments.