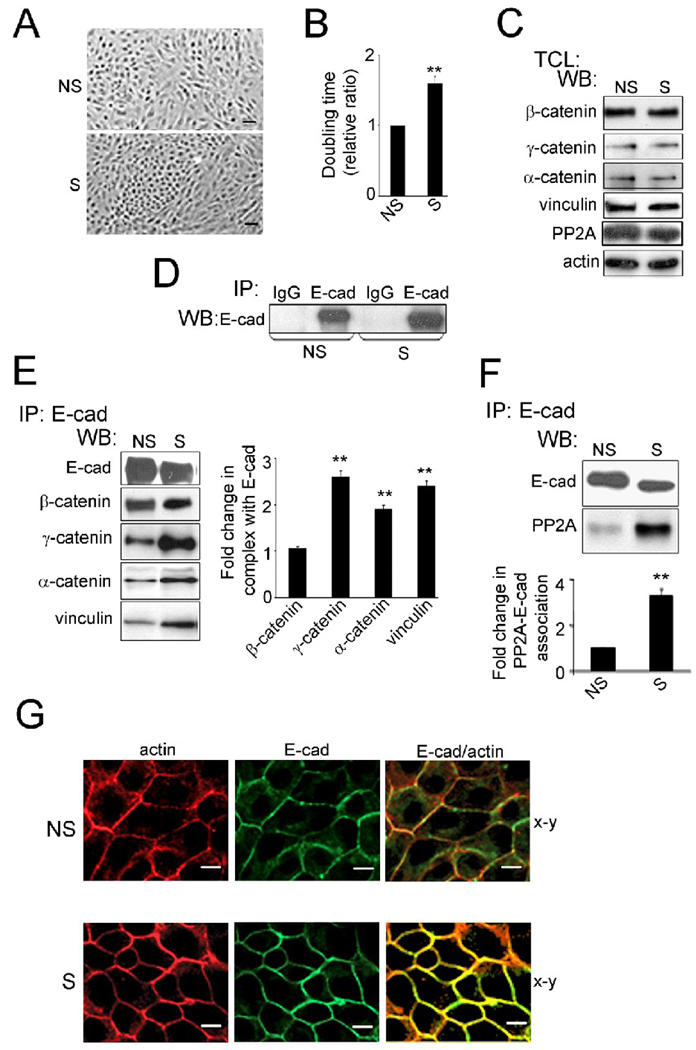
Fig. 3.
Partial silencing of DPAGT1 enhances AJs in MDCK cells. (A), Phase-contrast images of non-silenced (NS) and silenced (S) cells. Size bars, 25 µm. (B), Doubling times of non-silenced (NS) and silenced (S) cells. (**P<0.01). (C), TCLs from non-silenced (NS) and silenced (S) cells were examined for different catenins, vinculin and PP2A in comparison to actin by WB using data from four independent experiments. (D), Controls for immunoprecipitation experiments. TCLs were immunoprecipitated with antibodies against IgG isotypes and analyzed for expression of selected proteins by WB. (E), E-cadherins were immunoprecipitated from non-silenced (NS) and silenced (S) cells and analyzed for association with β-catenin, γ-catenin, α-catenin and vinculin by WB. Fold changes in protein levels associated with E-cadherin complexes from silenced (S) cells were determined in comparison to E-cadherin complexes from non-silenced (NS) cells after normalization to E-cadherin abundance with data from three independent experiments (**P<0.01). (F) E-cadherins were immunoprecipitated from TCL of non-silenced (NS) or silenced (S) cells, and their association with PP2A was assessed by WB. Fold change of PP2A protein levels from silenced (S) cells was determined in comparison with non-silenced (NS) cells after normalization to E-cadherin using data from three independent experiments (**P<0.01). (G) Non-silenced (NS) or silenced (S) cells were grown to confluence and processed for indirect immunofluorescence staining using an antibody to the cytoplasmic region of E-cadherin. Cells were counterstained for F-actin with rhodamine-phalloidin. Shown are 0.74 µm confocal x-y sections. Enhanced lateral colocalization of E-cadherin and F-actin in S cells compared to NS is highlighted in x–z sections. Size bars, 10 µm.