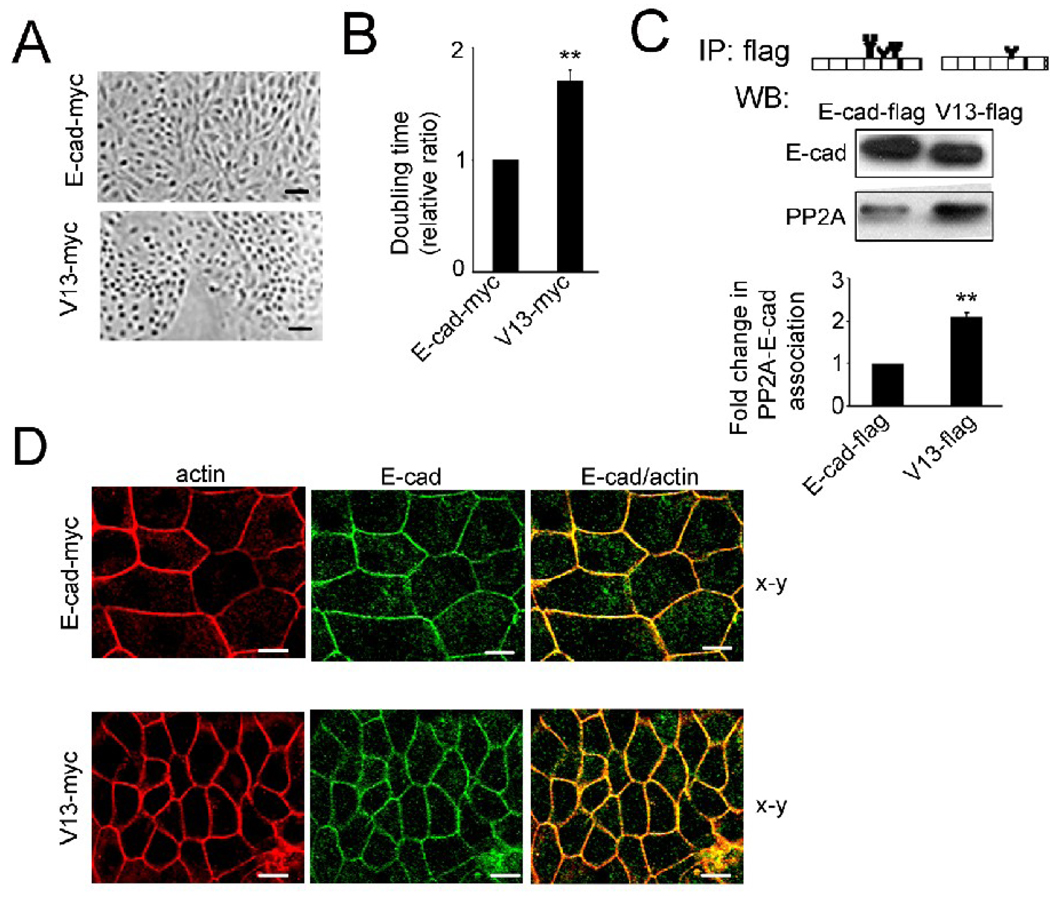
Fig. 4.
Hypoglycosylated E-cadherin enhances intercellular adhesion in MDCK cells. (A), Phase-contrast images of cells transfected with either wild type E-cadherin (E-cad-myc) or V13 (V13-myc). Size bars, 25 µm. (B), Doubling time of MDCK cells transfected with E-cad-myc and V13-myc. (**P<0.01). (C), Exogenous E-cadherins were immunoprecipitated from MDCK cells transfected with either wild type E-cadherin (E-cad-flag) or V13 (V13-flag) and examined for association with PP2A by WB. Fold change of PP2A protein level from V13-flag-transfected cells was determined in comparison with E-cad-flag-transfected cells after normalization to E-cadherin in three different experiments (**P<0.01). (D), Cells, transfected with E-cad-myc and V13-myc, were cultured in the presence of G418 to enrich for exogenous E-cadherins. Cells were immunostained for exogenous E-cadherins using an antibody to the myc tag, counterstained for F-actin with rhodamine phalloidin and examined by confocal microscopy. The images reflect 60% of cells expressing exogenous E-cadherin from a total population of 5×105 cells. Shown are 0.74 µm thick confocal x-y sections. Size bars, 10 µm. The images represent one of three independent experiments.