Fig. 6.
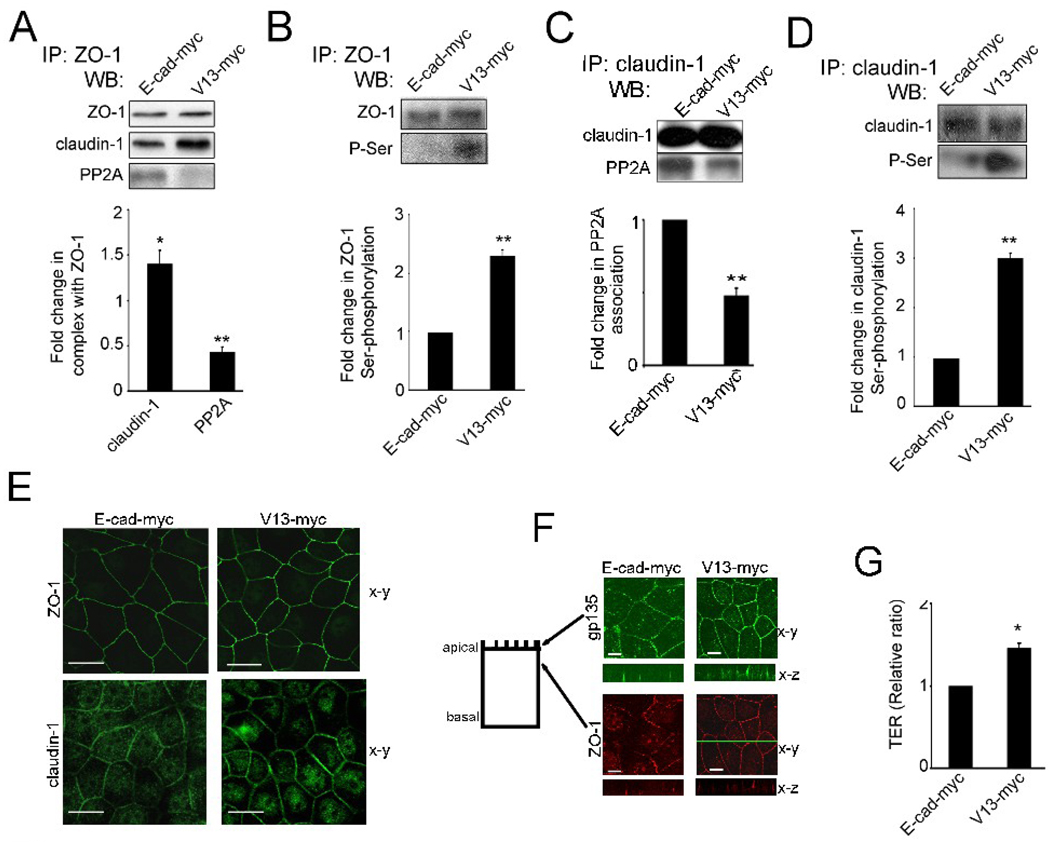
Hypoglycosylated E-cadherin drives the assembly of TJs. (A), ZO-1 was immunoprecipitated from cells transfected with either wild type E-cadherin (E-cad-myc) or V13 (V13-myc), and examined for association with claudin-1 and PP2A by WB. Fold changes in claudin-1 and PP2A levels in complex with ZO-1 in V13-myc-transfected cells were determined in comparison with E-cad-myc-transfected cells after normalization to ZO-1, based on data from three different experiments (*P<0.02;**P<0.01). (B), Fold changes in ZO-1 Ser-phosphorylation levels from V13-myc transfected cells were determined in comparison with E-cad-myc cells after normalization to ZO-1, using data from three different experiments (**P<0.01). (C), Fold changes in PP2A levels in complex with claudin-1 in V13 transfectants were determined in comparison with E-cad transfectants after normalization toclaudin-1, based on data from three different experiments (**P<0.01). (D), Fold changes in claudin-1 Ser-phosphorylation levels from V13-myc transfected cells were determined in comparison with E-cad-myc transfected cells after normalization to claudin-1 with data from three different experiments (**P<0.01). (E), Immunofluorescence localization of ZO-1 and claudin-1. Shown are 0.74 µm thick confocal x-y sections. Size bars, 10 µm. Images represent one of three independent experiments. (F), Immunofluorescence localization of gp135 and ZO-1 in E-cad and V13 transfectants. Shown are 0.74 µm thick confocal x-y sections, with x–z sections at indicated x-y positions (green line). Size bars, 10 µm. Images represent one of three independent experiments. (G), TER was measured in confluent monolayers of E-cad-myc and V13-myc transfected cells, with the value for TER from E-cad-myc cells defined as 1. Data were obtained using duplicate samples from four different experiments (*P < 0.02).