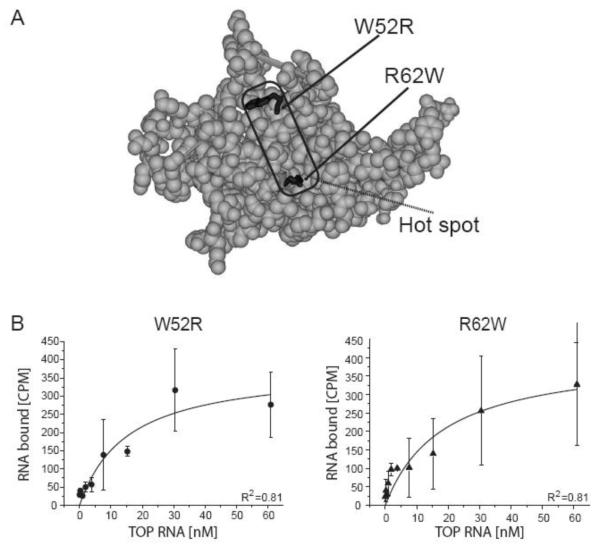
Figure 5.
rRPS19 protein variants with two DBA associated missense mutations (W52R, R62W) show reduced binding to the 5′UTR of RPS19 mRNA.
(A) Three-dimensional structure model of RPS19 [6]. The region with the most frequent mutations in DBA (for details see [9]) are indicated and the side chains of the mutations analyzed are highlighted in black. Residues are numbered according to human RPS19. (B) The equilibrium binding constant was determined using filter binding for rRPS19[W52R] and rRPS19[R62W] using the wild type TOP RNA substrate. The average ± standard deviation of three independent experiments was plotted and KDs were calculated using Origin®7.0. Both mutant proteins show a significantly reduced binding capacity compared to wild type protein (p<0.05; see table 2). The correlation coefficients are indicated (R2).