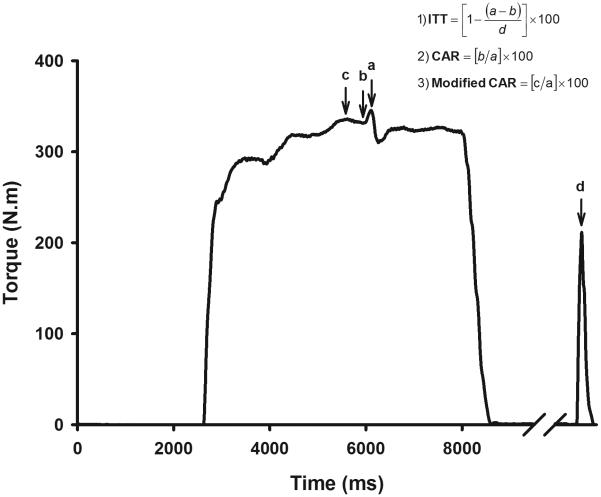
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the quantification techniques used to estimate voluntary quadriceps muscle activation. Incomplete activation of the quadriceps muscle is visualized by the increment in torque associated with the superimposed electrical pulses. When estimating percent voluntary activation based on the ITT, the user expresses stimulus evoked torque during contraction as a percentage of stimulus evoked torque at rest. When using the CAR method, the user estimates voluntary activation by comparing the voluntary torque at the time of stimulus delivery with the peak torque evoked with electrical burst superimposition. When using the modified CAR method, the user estimates voluntary activation by comparing the voluntary peak torque at any time prior to the stimulus delivery with the peak torque evoked with electrical burst superimposition. (a = peak torque evoked due to the superimposition of the electrical pulses, b = voluntary torque at the time of stimulus delivery, c = voluntary peak torque any time prior to the stimulus delivery, & d = stimulus evoked torque at rest).