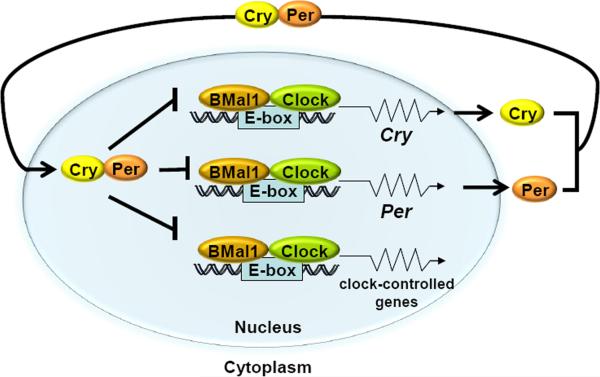
Figure 2.
Mammalian molecular clock. The bHLH-PAS domain-containing proteins Clock and BMal1 make a heterodimer which bind to the E-boxes (CACGTG) in the promoters of the Per and Cry genes, as well as in the promoters of the clock controlled genes, such as the excision repair gene Xpa and the checkpoint gene Wee1, activating their transcription. The Cry and Per proteins dimerize and, after a time lag, enter the nucleus and inhibit Clock-BMal1-activated transcription of their own genes as well as of those of clock-controlled genes, thus generating an oscillatory pattern of gene expression. Modified from [67].