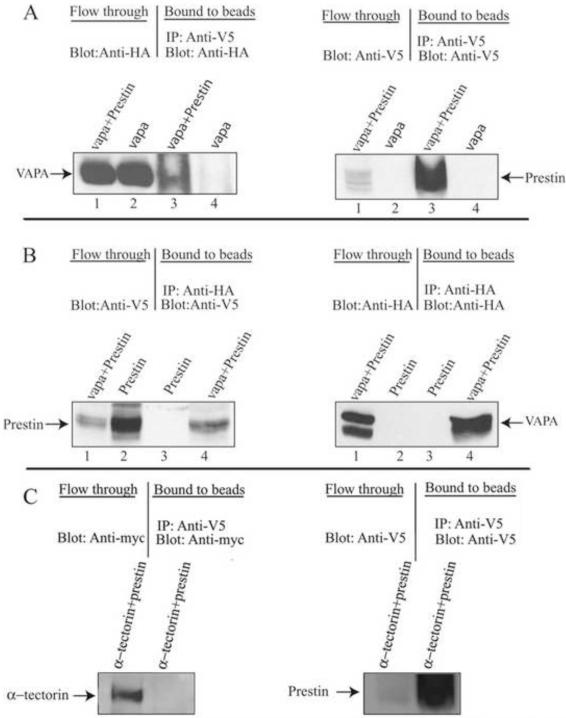
Figure 1.
VAPA can specifically bind to prestin. HEK293T cell lysates from HA-VAPA and V5-prestin+HA-VAPA or V5-prestin and V5-prestin+HA-VAPA-expressing cells were subjected to co-IP with anti-V5 or anti-HA and Protein A sepharose, respectively. A. The co-IP of HA-VAPA and V5-prestin where VAPA was immunoprecipitated with V5-prestin and VAPA was visualized by anti-HA antibody. The presence of prestin in the eluate was also shown by staining with anti-V5 antibody. Lanes 1 and 2 show proteins from flow-through. Lanes 3 and 4 are eluates from prestin-anti-V5-beads. B. The co-IP of HA-VAPA and V5-prestin where prestin was immunoprecipitated with HA-VAPA and prestin was visualized by anti-V5 antibody. The presence of VAPA in the eluate was shown by staining with anti-HA antibody. Lanes 1 and 2 show proteins from flow-through. Lanes 3 and 4 are eluates from VAPA-anti-HA-beads. C. The negative control. The co-IP of myc-α-tectorin and V5-prestin shows that no α-tectorin was present in the eluate from prestin-anti-V5-beads when blotted with anti-myc antibody whereas α-tectorin protein is present in the flow-through. The presence of prestin in the eluate was shown by staining with anti V5 antibody.