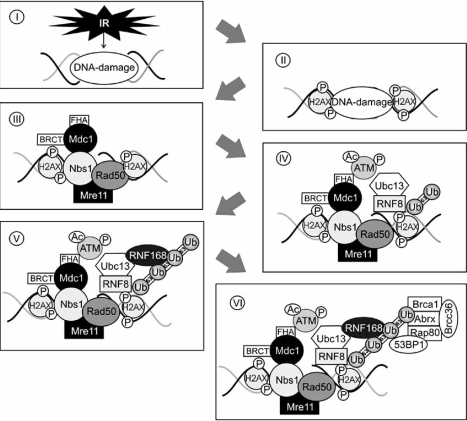
Fig. (3).
DNA lesion recognition and recruitment of repair factors. After introduction of a DNA double strand break (I), the DNA damage response is initiated by phosphorylation of H2AX (II), which is required for the recruitment of mediator proteins such as MDC1 or the MRN complex. MDC1 attaches to phosphorylated H2AX via its BRCT domain and stabilizes the MRN complex (III). Additionally it is responsible for binding and accumulation of ATM at the DSB, which creates a docking site for RNF8/Ubc13 that also associates with phosphorylated H2AX and decorates histone proteins with lysine 63-linked ubiquitin molecules (IV). RNF168 recognizes the initial ubiquitin chains generated by RNF8 and, in association with Ubc13, extends and propagates lysine 63-linked ubiquitination (V) that is required for the accumulation of additional repair factors like Bcra1 or 53BP1 (VI).