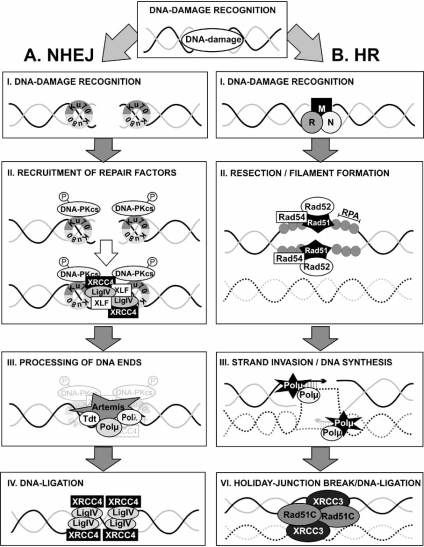
Fig. (4).
Mechanisms of DNA-repair by NHEJ and HR. Double strand breaks are repaired by two major pathways: non-homologous endjoining (A, NHEJ) and homologous recombination (B, HR). NHEJ: Loose DNA-ends are recognized by the Ku70/80 heterodimeric complex (A.I), which is needed for the recruitment of the additional repair factors DNA-PKcs, XRCC4, LigIV and XLF (A.II). Before broken DNA ends can be ligated, the ends are processed by Pol µ and λ, Artemis and Tdt (A.III). This step is followed by the ligation of the loose ends by LigIV and XRCC4 (A.IV). HR: HR is initiated by the MRN complex (B.I), followed by the recruitment of RPA that associates with single stranded DNA, and by Rad51/52 which are needed for filament formation and strand invasion (B.II). New DNA is synthesized while the homologous sister chromatid serves as a template (B.III). After branch migration, the holiday junction is resolved (B.IV).