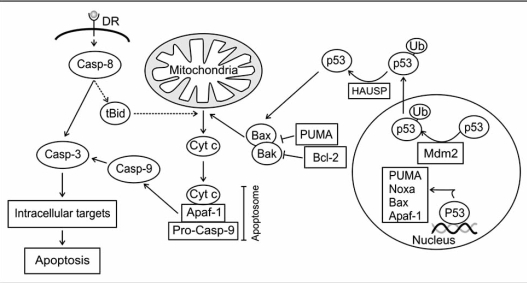
Fig. (5).
Apoptosis signaling pathways. Apoptosis can be induced upon activation of death receptors (DR) at the membrane by binding of cognate ligands or after release of pro-apoptotic factors from mitochondria. Upon DR activation, the initiator-caspase-8 becomes activated, which activates a caspase-cascade, and cleaves the pro-apoptotic proteins Bid. The cleavage of Bid results in the formation of active tBid, which, in cooperation with Bax and Bak, forms pores in the outer mitochondrial membrane resulting in the release of cytochrome c, formation of the apoptosome and activation of caspase 9. Caspases 9 activates caspase 3 leading to the degradation of intracellular targets. The proapoptotic proteins Bax and Bak can be inhibited by Bcl-2 and Puma. Besides its nuclear function p53 can become monoubiquitinated in a Mdm2-dependent manner, which leads to the translocation of p53 to mitochondria where it participates in mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and cytochrome c release.