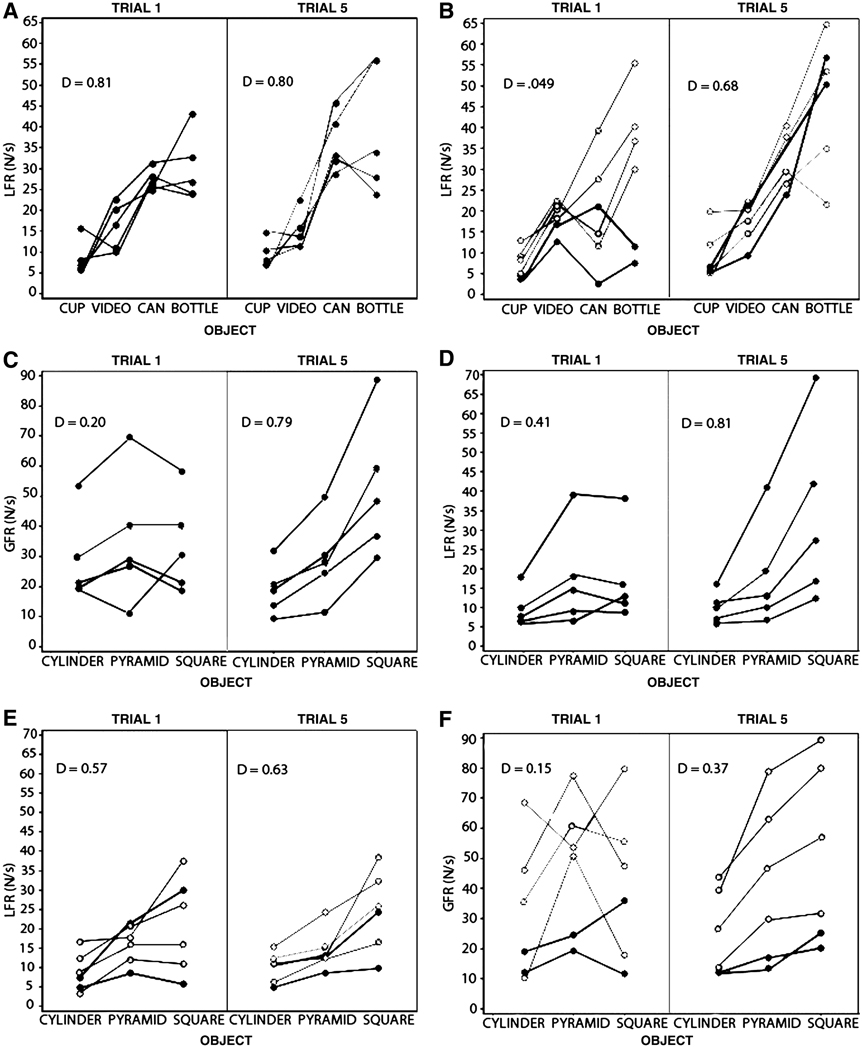
Fig 2.
Somers’ Dmeasure of association between real object weight and fingertip force. Each participant’s force rate is plotted by object and objects are ordered by ascending weight from left to right along the x-axis. Given that the x-values are ordered, Somers’ D is the difference between concordant and discordant pairs, divided by the number of concordant, discordant and tied pairs for the x-value. (A) Control LFR for familiar objects on Trials 1 and 5. (B) Patient LFR for familiar objects on Trials 1 and 5. Apraxics are demarcated by dark filled circles and non-apraxics by open circles. (C) Control GFR for novel objects on Trials 1 and 5. (D) Control LFR for novel objects on Trials 1 and 5. (E) Patient GFR for novel objects on Trials 1 and 5. (F) Control LFR for novel objects on Trials 1 and 5.