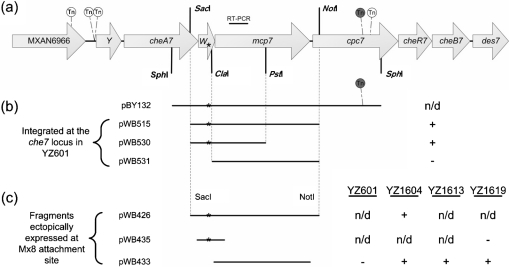
Fig. 1.
(a) Schematic of the M. xanthus che7 locus and transposon (Tn) insertions. The che7 locus shown here is ∼13 kb long. Gene lengths, Tn insertion sites and restriction sites are all drawn to scale. Shown are five independent Tn insertions that eliminated EPS production in the suppressor strain YZ101. These insertions starting from the left to right are designated MXAN6966 : : magellan4, cheY7-1 : : magellan4, cheY7-2 : : magellan4, cpc7-1 : : magellan4 and cpc7-2 : : magellan4 (Table 1 and Supplementary Table S1). Genomic DNA from strain BY132 (Table 1), which contains cpc7-1 : : magellan4 (shaded grey), was used to construct pBY132. The target for RT-PCR shown in Fig. 4 is shown above mcp7. (b) Indicated plasmids were transformed into YZ601 (ΔdifA) and integration occurred by homologous recombination at the che7 locus. ‘+’ and ‘−’ indicate that 5–10 % of the transformants were EPS+ or that 100 % of the transformants were EPS−, respectively, as determined by Congo red binding; ‘n/d’, not determined. (c) Listed expression plasmids were integrated at the Mx8 attachment site into the strains listed on the right: YZ601 (ΔdifA), YZ1604 (ΔdifA ΔcheW7 Δmcp7), YZ1613 (ΔdifA cheW7-1 Δmcp7) and YZ1619 (ΔdifA ΔcheW7). ‘+’ and ‘−’ indicate EPS+ or EPS−, respectively, as determined by Congo red binding. The asterisks mark the approximate location of the cheW7-1 mutation in all panels. cpc7 is predicted to encode a phycobilisome (PBS) lyase HEAT-like repeat protein (Arshinoff et al., 2007; Goldman et al., 2006). It is likely that there are promoters in the che7 locus, one upstream of MXAN6966 or cheY7 and another within cheW7 (see text for details).