Figure 3. VEGF and A23187 ionophore induce cytoplasmic-nuclear translocation of NFAT, whereas EGF fails to activate NFAT.
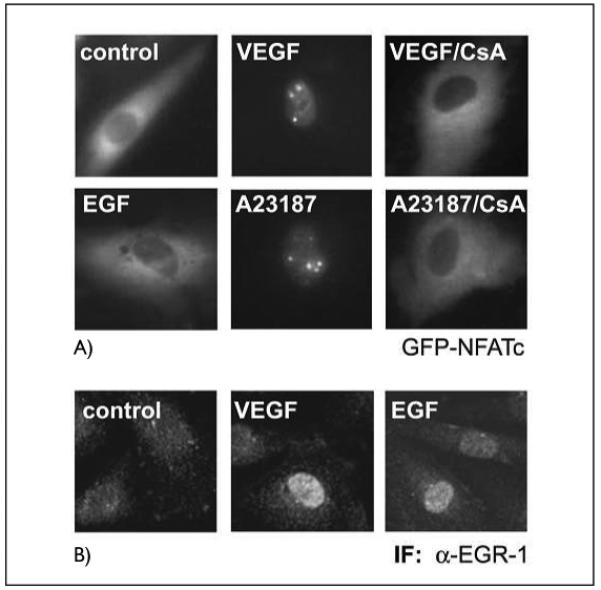
A) Cytoplasmic-nuclear transfer of a GFP-NFATc fusion protein. HUVE cells were transfected with an expression construct for a GFP-NFATc fusion protein. Twenty-four h post transfection the cells were induced with VEGF (100 ng/ml), EGF (10 ng/ml) or A23187 (2.5 μM) for 45 min. Where indicated, cells were preincubated with CsA (1 μg/ml) for 30 min prior to stimulation. Cytoplasmic-nuclear transfer was monitored in a Nikon fluorescence microscope equipped with a BM510 (B-2A) filter. B) Immunofluorescence of nuclear accumulation of EGR-1. HUVEC were treated with VEGF or EGF for 45 min, then the cells were fixed, permeabilized and stained using an anti-EGR-l antibody and a FITC-conjugated secondary antibody as described in Materials and methods.
