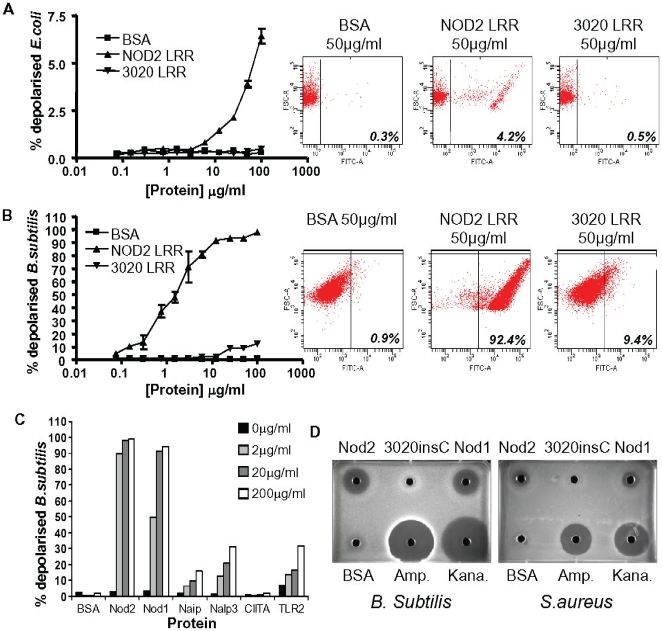
Figure 3. Bacterial killing by purified Nod2 LRR domains is deficient in the Crohn's-associated Nod2 3020insC mutant.
Results shown are all representative of several experiments. A,B, Nod2 LRR domains influence the membrane polarity of E.coli and B.subtilis. Proteins were added at the concentration indicated to 5×105 bacteria in 100 µL growth medium and incubated for 2 hours at 37°C. 15 minutes prior to the end of the time course, 50 µl of 10 µg/ml DiBAC4 solution was added to each well. Plates were washed twice with 750 µl ice cold PBS/well. The percentage of depolarised bacteria taking up the dye was determined by flow cytometry. C, Anti-bacterial activity of Nod1 and Nod2 but not Nod2 3020insC LRR domains demonstrated by agar diffusion assay. Agar plates were inoculated with a lawn of the indicated bacteria. Approximately 0.5 cm diameter holes were punched into the agar with a sterile glass pipette and the indicated protein (BSA protein control or indicated LRR domain) or antibiotic (ampicillin or kanamycin) added to each well at a concentration of 0.5 mg/ml in sterile PBS. D, B. subtilis membrane polarity is influenced by the LRR domains from a range of pattern-recognition receptors. Bacteria were treated with the indicated LRR domains as described for Figure 3a and their effect on the membrane polarity of the bacteria evaluated.