Figure 1. Overview of method for generation of HIV-specific human antibodies.
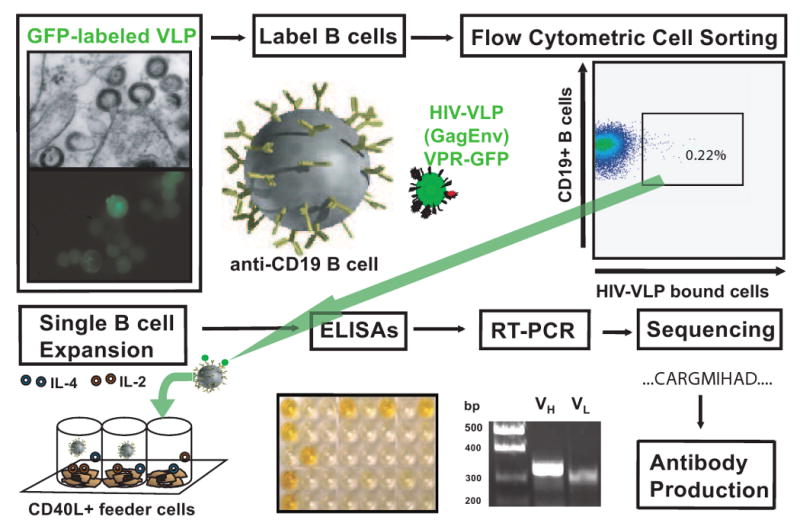
In the upper portion of the figure, HIV-VLPs are created in inducible cell lines and are shown here budding from the cell surface (by electron or fluorescent microscopy). B cells then are labeled with the resulting fluorescent HIV-VLPs and are shown here specifically labeling a subset of HIV-specific B cells from a HIV+ subject. These VLP-labeled B cells then are sorted into individual culture wells of a 96-well plate containing a stimulator cell line and cytokine mixture (shown in bottom portion of figure). ELISAs are used to identify clonal B cell populations HIV-specific immunoglobulins. Cells are collected from wells of interest, RNA isolation is performed and RT-PCR is used to clone the corresponding antibody variable gene segments of the heavy and light chains. Antibody genes of interest are sequenced and cloned into a plasmid based antibody expression system.
