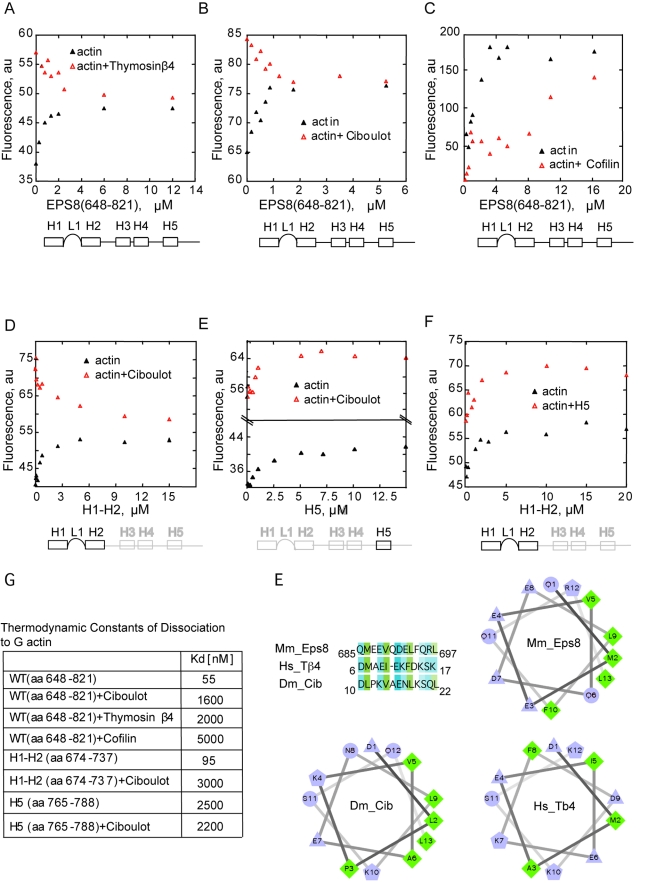
Figure 3. Eps8(648–821), Thymosin β4, Ciboulot, and ADF/Cofilin share common binding surfaces on actin.
(A–C) Eps8(648–821) competes with Thymosin β4 and Ciboulot for binding to monomeric actin. The change in fluorescence of 1.5 µM NBD-labeled-actin was measured in the presence of the indicated, increasing concentrations of Eps8(648–821) and/or saturating amounts (25 µM) of either Thymosin β4 (A) or Ciboulot (B), or ADF/Cofilin (C) in low salt buffer (G-buffer). In the case of ADF/Cofilin (C), NBD-ADP-actin was used. (D, E) H1–H2 but not H5 compete with Ciboulot for actin binding. The change in fluorescence of 1.5 µM NBD-labeled-actin was measured in the presence of the indicated, increasing concentrations of Eps8 helices (H1–H2, left or H5, right) alone or together with saturating amounts (25 µM) of Ciboulot, in low salt buffer (G-buffer). (F) H5 and H1–H2 do not compete for binding to monomeric actin. Change in fluorescence of NBD-labeled-actin in the presence of increasing concentrations of Eps8 helices (H1–H2) alone or together with saturating amounts (25 µM) of Eps8(H5) in low salt buffer (G-buffer). (G) Kinetic constants of dissociation of various fragments of Eps8 alone or in combination with the indicated actin binding proteins in low salt buffer (G-buffer) (see also Figure S2A–S2B for competition of Eps8(648–821) and H1–H2 with Thymosin β4 in high salt buffer). The Kds are calculated by fitting the data in (A–F) using Equation 1. (H) Helical wheel analysis of the predicted helix H1 of EPS8. Alignment of mouse Eps8 H1 helix with the WH2 domains of either human Thymosin β4 and Drosophila Ciboulot is shown on top left. Helical wheel analysis of the amphipathic helices of mEps8, hThymosin β4, and DCiboulot. The helix is projected along its axis going into the page. The hydrophilic residues are presented as circles, hydrophobic residues as diamonds, potentially negatively charged as triangles, and potentially positively charged as pentagons. Hydrophobicity is color coded as well: the most hydrophobic residue is green, and the amount of green is decreasing proportionally to the hydrophobicity, with zero hydrophobicity coded as yellow. Hydrophilic residues are coded blue with the potentially charged residues in light blue.