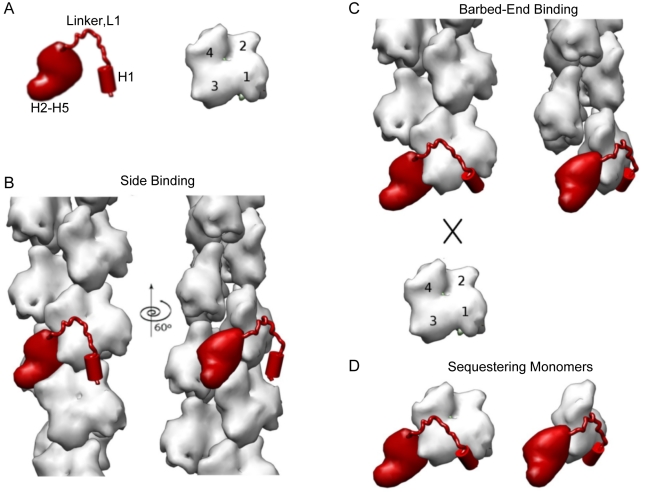
Figure 9. A schematic model for the binding modes of Eps8 to actin.
(A) A cartoon representation of Eps8 actin binding region and monomeric actin. The N-terminal amphipathic helix, H1, the connecting linker, L1, and the globular helical core, H2–H5, of Eps8 actin binding region are indicated. Monomeric actin is oriented with its barbed end downwards. Actin subdomains are numbered from 1 to 4. (B) Binding of Eps8 C-terminal region to the side of actin filament is mainly mediated by the globular helical bundle (H2–H5). The helical bundle (H2–H5) positions in the long grove of the filament, contacting three actin subunits. The amphipathic helix (H1) does not contribute significantly. The H1 binding site may not be fully exposed in filamentous actin. (C) At the barbed ends, the H1 binding site is fully accessible and H1 can bind within the hydrophobic pocket blocking further addition of monomeric actin. (D) A similar arrangement as seen at the barbed end is presumably occurring on monomeric actin, accounting for the sequestering activity of Eps8. In (B–D), two views, related by a 60° counterclockwise rotation around the filament axis, are shown.