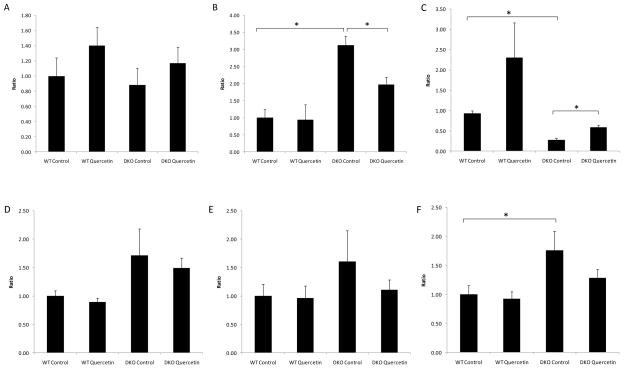
Figure 7. Quercetin treatment could not effectively suppress the increased ocular transcription of pro-apoptotic factors in DKO mice.
Quercetin in the vehicle (40% v/v DMSO/PBS) was injected intraperitoneally (25mg/kg/day) for two months. Equivalent volumes of solvent were delivered intraperitoneally to the control vehicle groups. After two months of treatment, the mice were sacrificed, and the eyes were enucleated and homogenized. Total RNA was isolated and converted to cDNA. RQ-PCR analysis was then performed to determine the levels of Bcl-2 (A), Bax (B), Bcl-2/Bax ratio (C), Fas (D), FasL (E) and Caspase-3 (F). Bars represent the mean ± S.E. (n ≥ 3) (*: p < 0.05)