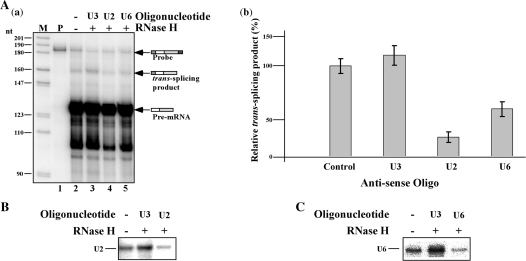
Figure 7.
RNaseH digestion of U2 or U6 snRNAs inhibits in vitro trans-splicing. (A) (a) Whole-cell extract was incubated for 1 h on ice with oligonucleotides complementary to U3, U2 or U6 snRNAs, in the presence of 1U RNase H, as described in ‘Materials and Methods’ section. The RNA from the different reactions was analyzed by an RNase protection assay. RNA was separated on a 6% sequencing gel. Lane contents are as follows: 1, Probe (500 c.p.m.); 2, RNA from in vitro trans-splicing extract (control); 3, extract was subjected to RNase H cleavage with U3-specific oligonucleotide; 4, extract was subjected to RNase H cleavage with U2-specific oligonucleotide; 5, extract was subjected to RNase H cleavage with U6-specific oligonucleotide. M-DNA marker, labeled pBR322 DNA MspI digest. (b) Quantitation of the effect on the production of the trans-spliced product; data represent three independent experiments. (B) Primer extension to determine the amount of U2 snRNA after RNase H treatment. Primer extension was performed on RNase H-oligonucleotide cleaved extracts using U2 specific primer (listed in S-1). The identity of the antisense oligonucleotides used for cleavage is indicated. (C) Primer extension to determine the amount of U6 snRNA after RNase H treatment. Primer extension was performed on RNase H-oligonucleotide cleaved extracts using U6 specific primer (listed in S-1). The identity of the antisense oligonucleotides used for cleavage is indicated.