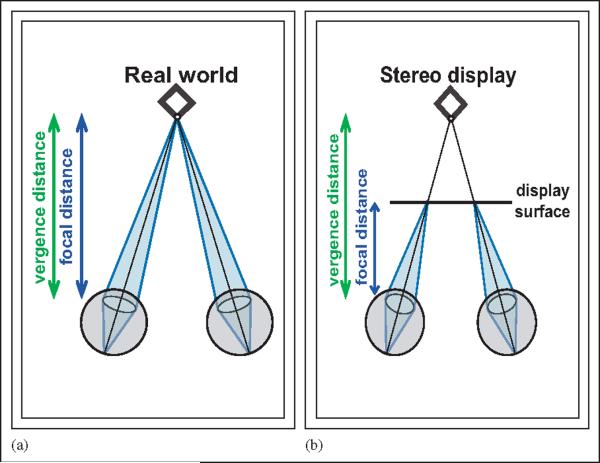
Fig. 1.
Vergence and focal distances with real stimuli and stimuli presented on conventional stereo displays. (a) Viewing an object in the real world. Vergence distance is the distance where the fixation axes of the two eyes converge. Focal distance is the distance to which the two eyes are focused. In the real world, vergence and focal distance are typically the same. (b) The same object viewed on a conventional stereo display. The display surface is nearer than the simulated object, so focal distance is shorter than vergence distance. Because focal distance is constant, vergence and focus distances match only for simulated objects at the focal distance.