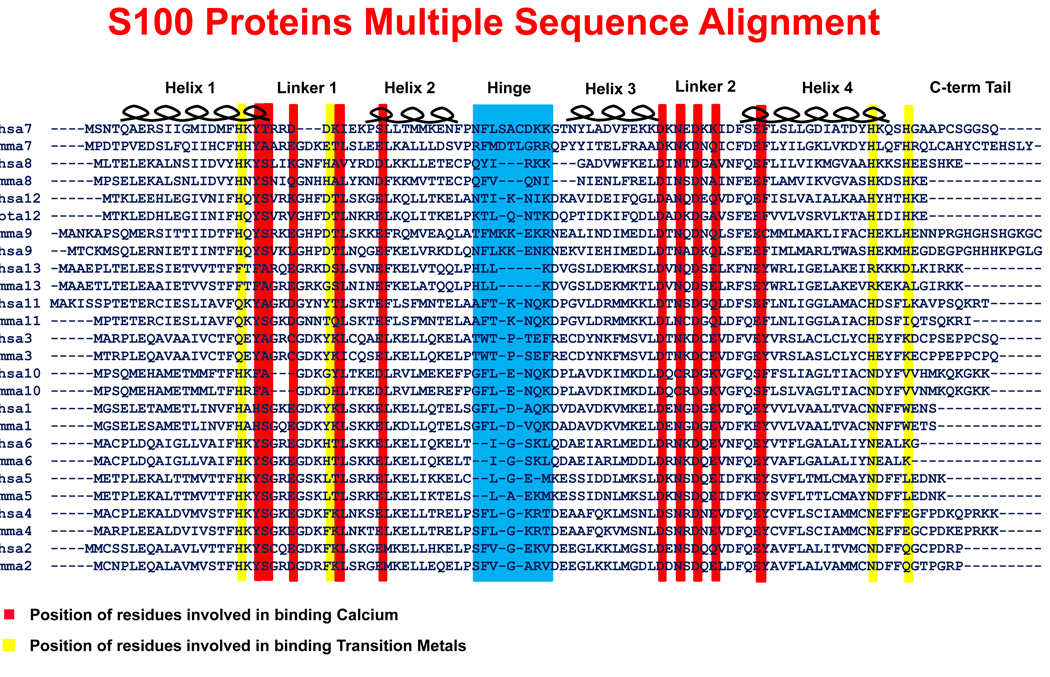
Figure 1. Multiple sequence alignment of S100 protein family.
A pair of sequences, mouse and human if available, for the S100A1 thru S100A13 proteins was used to generate the alignment. The common features of the S100 proteins are the first EF Hand (containing helices 1 & 2 as well as the linker 1 region), the hinge region, the second EF Hand (containing helices 3 & 4 as well as the linker 2 region), and the carboxy-terminal tail. A red background indicates the locations of the residues responsible for binding calcium. Although no S100 monomer is able to bind a transition metal, a pair of yellow lines indicates the location of the residues that create each half of the transition metal binding site within a dimer. The hinge region is highlighted in blue. The hinge region and helix 3 in S100A8 are shortened relative to other S100 proteins.