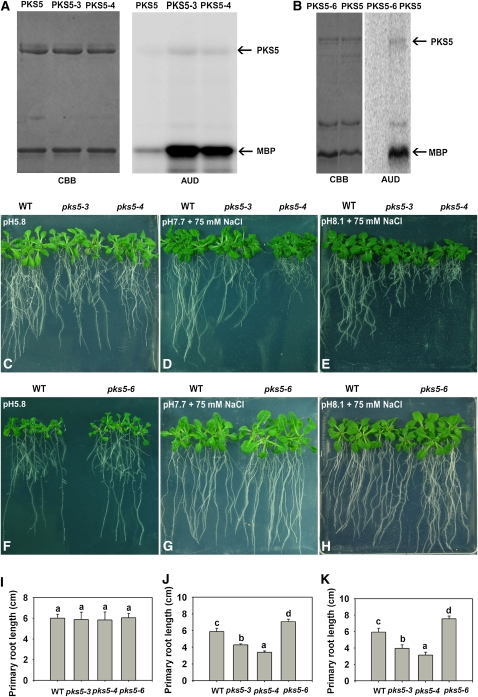
Figure 6.
PKS5 Kinase Activity Negatively Correlates with PM H+-ATPase Activity and Seedling Sensitivity to Salt in Alkaline Conditions.
(A) and (B) Kinase activity comparison for the PKS5, PKS5-3, PKS5-4, and PKS5-6 proteins. Left panel: Coomassie blue (CBB)–stained SDS-PAGE gel containing the PKS5 wild-type and mutant proteins and the substrate, MBP. Right panel: autoradiograph (AUD) of kinase activity assays shown in the left panel.
(C) to (H) Five-day-old wild type (Col er105), pks5-3, pks5-4, and pks5-6 seedlings grown on MS medium at pH 5.8 were transferred to MS medium at pH 5.8, at pH 7.7 with 75 mM NaCl, or at pH 8.1 with 75 mM NaCl. Photographs in (C) and (F) were taken 7 d after transfer; in (D) and (G), 14 d after transfer; and in (E) and (H), 21 d after transfer.
(I) Primary root elongation of seedlings transferred to MS medium at pH 5.8.
(J) Primary root elongation of seedlings transferred to MS medium at pH 7.7 with 75 mM NaCl.
(K) Primary root elongation of seedlings transferred to MS medium at pH 8.1 with 75 mM NaCl.
In (I) to (K), primary root length was measured 7, 14, and 21 d after transfer, respectively. Error bars represent sd (plant number >15). A Student's t test was used for determining the statistical significance; significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) in (I) to (K) are indicated by different lowercase letters.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]