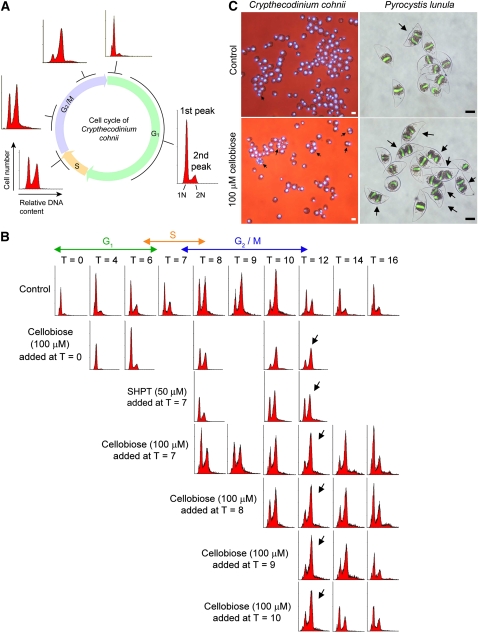
Figure 1.
Cellobiose Delayed the C. cohnii Cell Cycle at the G2/M Phase.
(A) A schematic diagram of DNA histograms showing the progression of the C. cohnii cell cycle from a population of synchronized G1 cells. The x axis of a DNA histogram represents the relative DNA content (propidium iodide [PI] fluorescence intensity), while the y axis represents the cell number (number of events). The first peak corresponds to the cells with the G1 DNA content (1N) and the second corresponds to the cells with the G2/M content (2N). In the G1 phase, the first peak (1N DNA content) appears as the major peak in a histogram. As the cells progress to the S phase, the first (G1, 1N) peak drops, and the second (G2/M, 2N) increases. During the G2/M phase, the DNA content doubles. Eventually, the cells complete mitosis and reenter the next G1 phase (the second peak drops and the first peak increases again).
(B) Flow cytograms of PI-stained synchronous C. cohnii. T refers to the time (hours) at which the samples were harvested after cell cycle synchronization at early G1. Cellulase inhibitors, cellobiose and SHPT, were added to synchronized cells at different time points to investigate the possible involvement of cellulase in cell cycle progression. Cellobiose (100 μM) was added at T = 0 (early G1), T = 7 (early G2), T = 8, T = 9, or T = 10 (late G2/M). SHPT (50 μM) was added at T = 7 (early G2). For control cells, the cells finished a cell cycle within 12 h (the first peak becomes the major peak again at T = 12). A G2/M delay, indicated by the arrows, was observed in cells treated with both cellobiose (added at T =0, 7, 8, 9, and 10) and SHPT (added at T = 7). It took longer for the cells to leave the G2/M phase and return to the G1 phase. This was revealed by the histogram with a higher second peak at T = 12 (indicated by the arrows) when compared with the control.
(C) Merged images of bright-field and fluorescence photomicrographs showing the effects of cellobiose (100 μM) on asynchronous C. cohnii and P. lunula. Cells were incubated with cellobiose for 24 h. DNA was stained blue with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole for C. cohnii and green with SYTOX Green for P. lunula. Arrows indicate the multinucleated cells. For C. cohnii, bars = 10 μm; for P. lunula, bars = 50 μm.
[See online article for color version of this figure.]