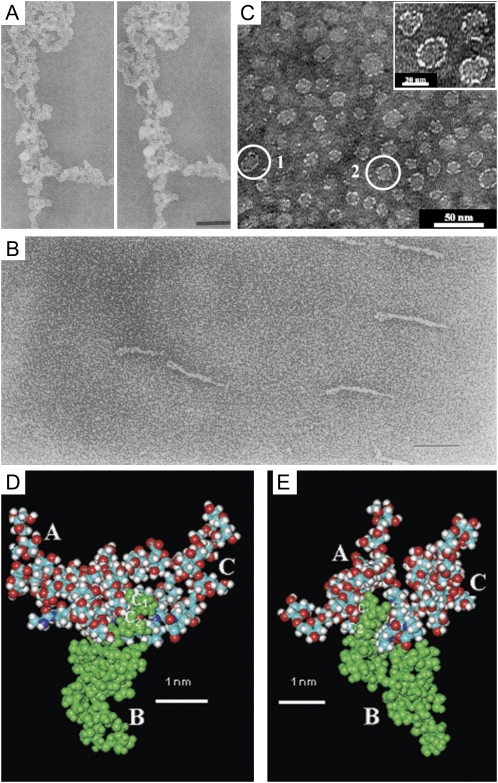
Figure 2.
A composite of images of AGPs purified from various plants. A, Stereopair of TEM micrographs showing the three-dimensional structure of a large aggregate of AGP from carrot suspension cultures imaged by the fast-freeze, deep-etch, rotary-shadowed replica technique. Bar = 200 nm. This image is from Baldwin et al. (1993). B, TEM micrograph of Superose-purified GAGP from gum arabic after rotary shadowing. Bar = 100 nm. This image is from Qi et al. (1991). C, TEM micrograph of the AG peptide F1 from acacia gum. The inset shows a magnification of part of the micrograph. This image is modified from Sanchez et al. (2008). D and E, Space-filling CPK models of three AHP-1 AGs (15 glycan residues per polysaccharide chain) from tobacco BY2 cells glycosidically linked to C-4 of each Hyp (O) residue in the 12-residue peptide (A-P-A-O-A-O-A-O-A-P-A-P), in which each O has an AHP-1 substitution (underlined). Nitrogen atoms are shown in dark blue; the oxygen atoms are red; hydrogen atoms are gray; and carbon atoms are turquoise blue. These images are from Tan et al. (2004). D, Glycosylated (A-O/P)6 (see above). Side view of a polysaccharide cluster. Three AHP-1 glycans labeled A to C are O-linked to the Hyp residues of the glycosylated (A-O/P)6 model (residues 4, 6, and 8 of the peptide). The protein backbone lies across the figure, with the N terminus at the far left. Note the close proximity of polysaccharide B (green) to the polypeptide backbone, where the Ara disaccharide residues C1 and C2 form three H bonds as follows: the hydroxymethyl (C-5) of Ara residue C1 to both the carbonyl of Hyp residue 4 and the peptide N of Ala residue 5; and the C-2 hydroxyl of Ara residue C2 to the NH of Ala residue 6. In contrast, the Ara trisaccharide residues at the tip of each polysaccharide form peripheral hook-like projections; these may result in multiple weak interactions (“molecular Velcro”) with the Yariv reagent, which specifically interacts with AGPs. E, Glycopeptide (A-O/P)6. End-on view of a polysaccharide cluster. Reorienting the polypeptide so that it is perpendicular to the plane of the paper shows a syndiotactic propeller-like arrangement of the AG polysaccharides around the polypeptide, providing surfaces for interactions and interdigitation with other matrix molecules.