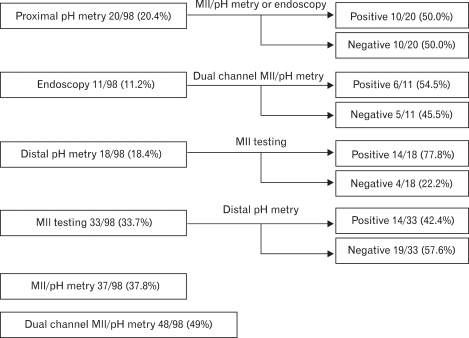
Figure 1.
Diagnostic yield of various methods for detecting gastroesophageal reflux. Diagnostic yield of proximal pH-metry, endoscopy, distal pH-metry, multichannel intraluminal impedance (MII) testing, MII/distal pH-metry, and dual channel MII/pH-metry was 20.4%, 11.2%, 18.4%, 33.7%, 37.8%, and 49.0%, respectively. Pathologic proximal acid reflux was seen in 10 patients without any evidence of distal gastroesophageal reflux (GER), and erosive esophagitis (EE) occured as a single phenomenon in 5 patients. Four patients with negative result on MII testing had pathologic acid GER, and 19 patients with negative result on distal pH-metry had abnormal finding with MII testing.