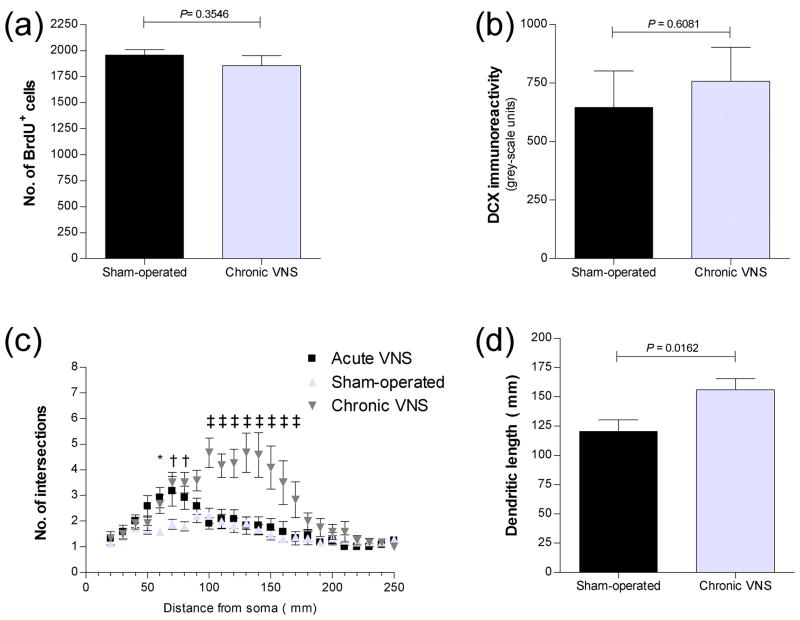
Figure 3.
Quantitation of newly generated cells (a) and effects of chronic VNS on the dendritic morphology of DCX+ neurons (b–f) in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampal formation after chronic VNS. (a) The number of BrdU+ cells in the subgranular zone and granule cell layer of the dorsal dentate gyrus was determined (as in Figure 1) 3 weeks after administration of VNS for 1 month. Data are means ± SEM of values from six rats per group. The P value for comparison between VNS-treated and sham-operated animals was determined by ANOVA followed by Scheffe’s test. (b) Quantitation of DCX immunoreactivity in the dorsal dentate gyrus 3 weeks after chronic VNS for 1 month. Data are means ± SEM of values from six rats per group. The P value for comparison with sham-operated animals was determined by ANOVA followed by Scheffe’s test. (c) Sholl analysis of apical dendrites of DCX+ neurons in the dorsal dentate gyrus of rats 3 weeks after acute or chronic VNS. The numbers of dendrites that cross the indicated radial distances (0 to 250 μm) from the soma are shown. Data are means ± SEM of values from six rats per group. *P < 0.05, †P < 0.01, ‡P < 0.001 versus corresponding sham-operated controls (Newman-Keuls test). (d) Dendritic length for DCX+ neurons in the dorsal dentate gyrus of rats 3 weeks after chronic VNS. Data are means ± SEM of values from six rats per group. The P value for comparison with sham-operated controls was determined by ANOVA followed by Scheffe’s test. (e–f) Representative immunofluorescence images of neurons positive for DCX or NeuN in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampal formation after chronic VNS. Sections of the dorsal dentate gyrus obtained from rats 3 weeks after chronic VNS (f) or from sham-operated controls (e) were stained with antibodies to DCX (red) or to NeuN (green). The boxed regions in the top panels are shown at higher magnification in the bottom panels. Note the increase in dendritic complexity and length for DCX+ neurons in rats subjected to VNS compared with those in control animals. The dendrites project deeply into the hippocampal molecular layer through the granule cell layer stained with the neuronal marker NeuN. Arrows in the merged images indicate that most DCX+ neurons were also positive for NeuN.