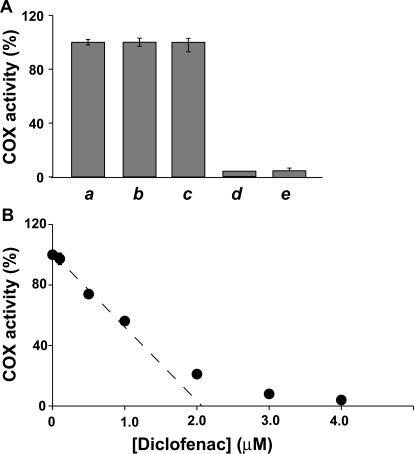
Fig. 1.
Time-dependent inhibition of native huPGHS-2 by diclofenac and indomethacin. Purified huPGHS-2 (2 μM) was pretreated with no inhibitor (a, b, and c) for 10 min at 37°C or 12 μM diclofenac (d) for 10 min at 37°C or 100 μM indomethacin (e) for 5 min at 37°C. No inhibitor was added to the O2 electrode assay chamber when the sample (a) was assayed. Diclofenac (0.16 μM) was included in the assay chamber when the sample (b) was assayed; sample b served as the negative control for sample d. Indomethacin (1.3 μM) was included in the assay chamber when sample c was assayed; sample c served as the negative control for sample e. Dilution of the aliquot of sample d yielded a final concentration of 0.16 μM diclofenac in the assay chamber, and no additional diclofenac was added to this assay chamber. Dilution of the aliquot of sample e yielded a final concentration of 1.3 μM indomethacin in the assay chamber, and no additional indomethacin was added to this assay chamber. Assays were performed at 37°C in 3 ml of 0.1 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, containing 100 μM arachidonic acid, 1 mM phenol, and 1 μM hematin. B, purified huPGHS-2 (2.1 μM) was pretreated with the indicated concentrations of diclofenac at 37°C for 10 min and then assayed for COX activity with 100 μM AA essentially as described above. Error bars show standard deviations from multiple kinetic trials.