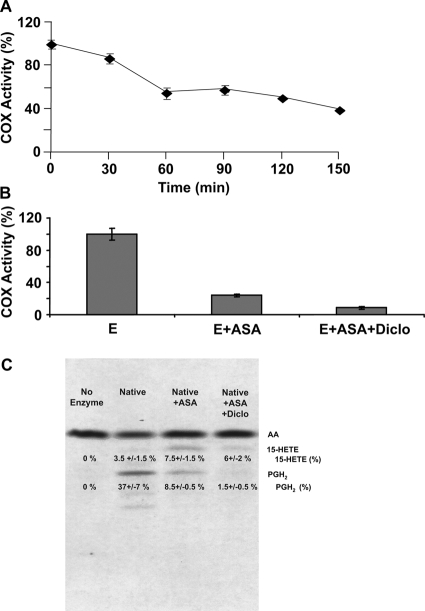
Fig. 2.
Inhibition of huPGHS-2 by aspirin. A, purified native huPGHS-2 homodimer was incubated at 24°C with or without freshly prepared aspirin (500 μM) for the indicated times and then assayed for COX activity using an O2 electrode. Values are derived from the average of triplicate determinations ± S.E. Similar experiments were performed at least three times with different preparations of enzyme and yielded quantitatively similar results. B, purified native huPGHS-2 was pretreated with 500 μM aspirin for 1 h at 37°C, which causes maximal inhibition. The sample was then incubated without (E + ASA) or with (E + ASA + Diclo) 12.5 μM diclofenac (Diclo) for 10 min and assayed for COX activity using an O2 electrode. For the samples pretreated with diclofenac for 10 min, the assay mixture also contained 12.5 μM diclofenac. A control with huPGHS-2 without inhibitor (E) was treated for 1 h at 37°C with vehicle (in place of aspirin) and then incubated for an additional 10 min without any inhibitor. C, purified native huPGHS-2 was incubated with or without ASA (500 μM) at 37°C for 1 h, and the oxygenation of [1-14C]AA was assayed by radio thin-layer chromatography in the presence and absence of 12.5 μM Diclo as described under Materials and Methods. Thin-layer chromatography was used to separate the endoperoxide (PGH2) and monohydroxy acid products, mainly 15-HETE. To perform the assays, [1-14C]AA (100 μM) was mixed with ∼9 μg of native huPGHS-2 in an assay volume of 0.10 ml, and the reactions were allowed to proceed for 40 s. The reactions were stopped, and the products were extracted, separated, and visualized by autoradiography as shown. The thin-layer plates were subsequently scraped, and the amount of radioactivity cochromatographing with AA, PGH2, and 15-HETE standards was determined by scintillation counting. Numbers obtained from scintillation counting were used to calculate the percentage of total radioactivity found in each product. The experiment was performed three times with consistent results.