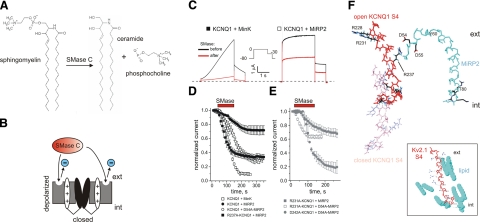
Figure 5.
R237-D54 interaction protects activated KCNQ1 S4 from the effects of membrane sphingomyelin hydrolysis. A) Hydrolysis of sphingomyelin by SMase. B) Cartoon of the Kv channel activated-S4-destabilizing effect of SMase. C) Exemplar traces before application and after washout of SMase for oocytes expressing KCNQ1 with MinK or MiRP2, using the voltage protocol shown. Dashed line indicates 0 current level. D, E) Rundown-normalized mean peak current at 0 mV before and during application and after washout of SMase, normalized to time 0 peak current, for oocytes expressing KCNQ1 and MiRP2 variants as indicated, using the protocol shown in C; n = 4–8/group. Red bar indicates SMase application. F) Hypothetical model indicating feasibility of R237-D54/55 interaction. Open and closed KCNQ1 S4 model coordinates are from ref. 28; MiRP2 was modeled (SwissModel) from the NMR structure of full-length MinK (28). Side chains are shown only for polar residues. MiRP2 Y60 and T80 indicate boundaries of proposed transmembrane domain (Fig. 1A). Inset: Kv2.1 S4 with nearby lipid molecules; coordinates from the crystal structure of Kv1.2/ Kv2.1 paddle chimera in lipid (2). ext, extracellular; int, intracellular.