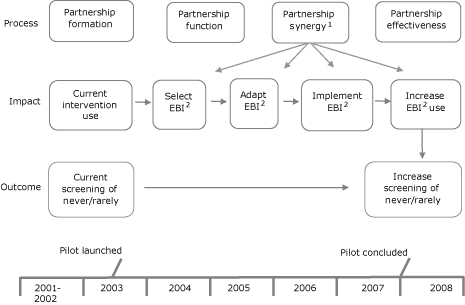
Figure 3.
Team Up evaluation organizational framework. Abbreviation: EBI, evidence-based intervention.
1. Partnership synergy is a collaborative process that enables a group of people and organizations to combine complementary knowledge, skills, and resources to accomplish more as a group than as individuals (Lasker and Weiss, 2003). The Lasker and Weiss Partnership Self-Assessment Tool identifies a partnership's strengths and weaknesses in areas known to be related to synergy: leadership, efficiency, administration and management, and sufficiency of resources. Response categories are based on 5-point Likert scales (extremely well [5] to not at all well [1]; excellent [5] to poor [1]; all of what it needs [5] to none of what it needs [1]). Overall synergy results are based on a compilation of definitive questions with the resulting categorical scores: Danger Zone (1.0-2.9) requires a lot of improvement; Work Zone (3.0-3.9) requires effort to maximize the partnership's collaborative potential; Headway Zone (4.0-4.5) encourages greater potential to progress further; and Target Zone (4.6-5.0) requires focus to maintain a synergistic partnership (http://partnershiptool.net/).
2. EBI: Evidence-based intervention. The term "evidence-based intervention" refers to an intervention that has been tested through randomly controlled experiments with efficacious results that have been published in peer-reviewed journals (http://www.aoa.gov/doingbus/fundopp/announcements/2008/ADDGS_Evidence_Based_FAQ.doc).
| This figure is titled “Team Up evaluation organizational framework.” There are 3 rows headed, from top to bottom, process, impact, and outcome. Items in the first row are partnership formation, partnership function, partnership synergy, and partnership effectiveness. Items in the second row are current intervention use, select EBI, adapt EBI, and implement EBI use. The third row has 2 components: to the left, current screening of never/rarely, and on the far right, increase screening of never/rarely. A timeline runs horizontally below, showing that the pilot was launched in the first quarter of 2003 and concluded at the end of 2007. Arrows in each row point from the first item in each row to the next, until the last item. Under the item partnership synergy, 4 arrows point to items in the next row: select EBI, adapt EBI, and implement EBI use. EBI is an abbreviation for evidence-based intervention. |
| The legend defines partnership synergy and evidence-based intervention. The legend says: |
|