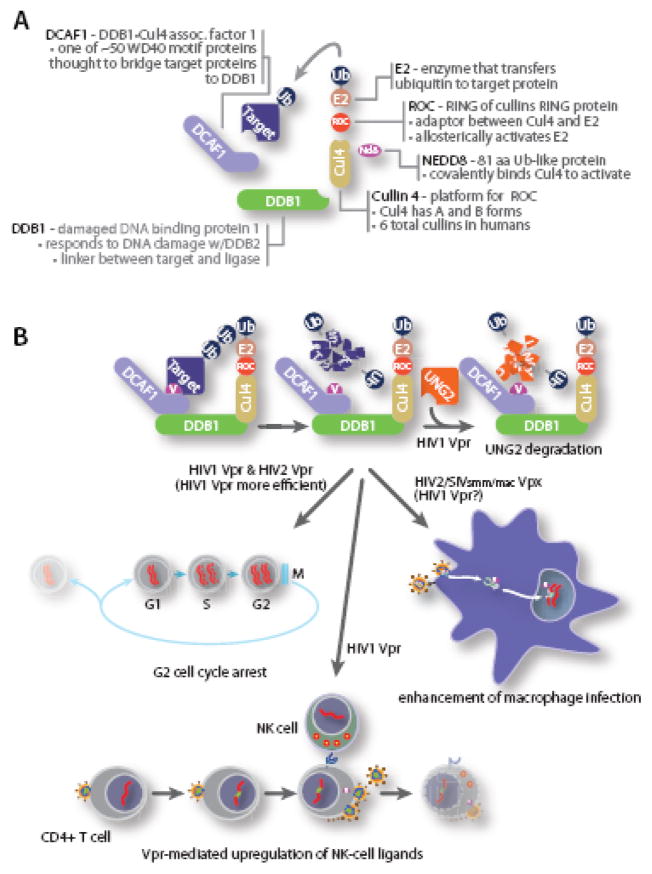
Fig. 2.
A. Overview of DCAF1•DDB1•Cul4 ubiquitin ligase complex. Cullin 4 assembles with a multi-subunit complex to ubiquitylate targeted proteins. Cul4 C terminus associates with a small RING protein, ROC, that recruits and activates an E2 enzyme, while the N terminus of Cul4 interacts with a linker protein, DDB1 that binds the adaptor protein, DCAF1 that interacts with HIV1 Vpr, HIV2 Vpr or HIV2/SIV Vpx. B. The role of the ubiquitin ligase complex in Vpr function. Evidence supports a model in which Vpr/Vpx directs the DDB1•Cul4 ubiquitin ligase complex to ubiquitinate (1) a cellular uracil N glycosylase, UNG2, (2) a cellular protein required for cell cycle progression into mitosis, (3) a cellular protein that is degraded to activate ATR signaling and increases cell surface NKG2D ligands to enhance NK cell-mediated killing, and (4) a cellular antiviral factor that inhibits viral reverse transcription in macrophages.