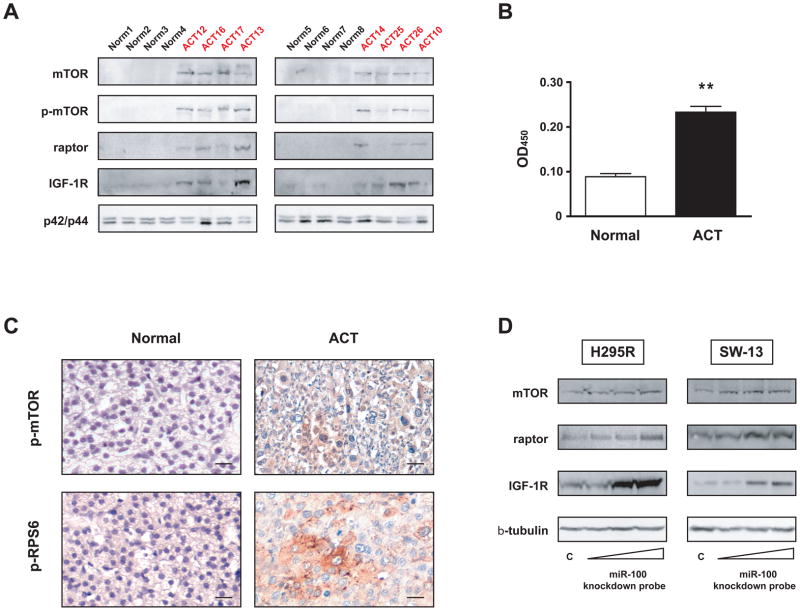
Figure 2. mTOR signalling is activated in childhood ACT and knockdown of endogenous miR-100 regulates expression of mTOR, raptor and IGF-1R proteins in adrenocortical tumor cells.
A, Immunoblot showing expression of mTOR, phospho-mTOR (Ser 2448), raptor and IGF-1R proteins in a series of 8 ACTs (ACT10, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 25, 26; see Supplementary Table 1 for patients’ clinical data) and 8 normal adrenal cortex samples. p42/p44 expression is shown as loading control. Quantification of immunoblot results is shown in Supplementary Figure 3. B, mTOR kinase activity against recombinant GST-p70S6K was measured in 8 ACTs (ACT7, 9, 11, 15, 16, 27, 28, 29; see Supplementary Table 1 for clinical data) and 3 normal adrenal cortex samples by EIA. ** p<0.01, Student’s t-test. C, Top, immunohistochemistry showing strong diffuse expression of phospho-mTOR (Ser 2448) in one ACT sample (ACT30; see Supplementary Table 1 for patients’ clinical data). Bottom, focal phospho-RPS6 (Ser240/244) staining in another ACT sample (ACT 32). 40X magnification, bar = 20 μm in all panels. Quantification of IHC results for each patient analyzed is shown in Supplementary Table 3. D, H295R (left) and SW-13 (left) tumor adrenocortical cells were transfected with increasing concentrations (10, 25 and 50 nM) of miR-100 knockdown probe or scramble control (50 nM). Expression of endogenous mTOR, raptor and IGF-1R proteins was revealed by immunoblot 48 hours after transfection. β-tubulin expression is shown as loading control.