Abstract
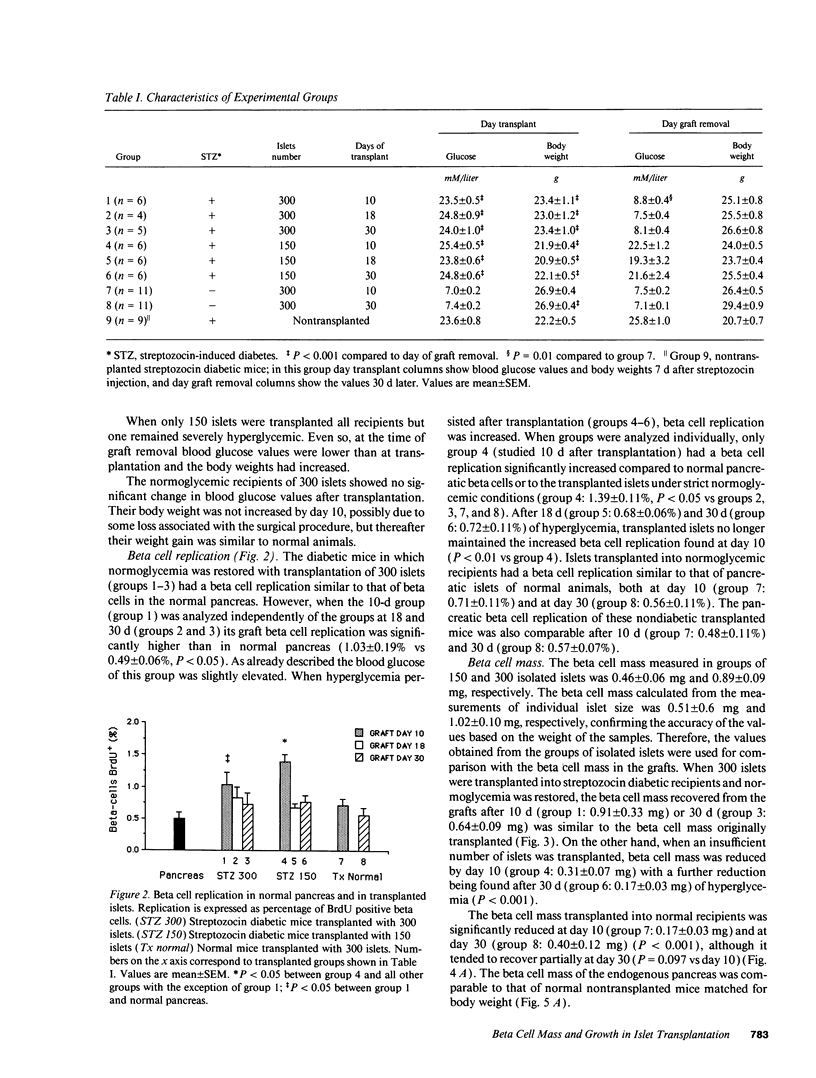
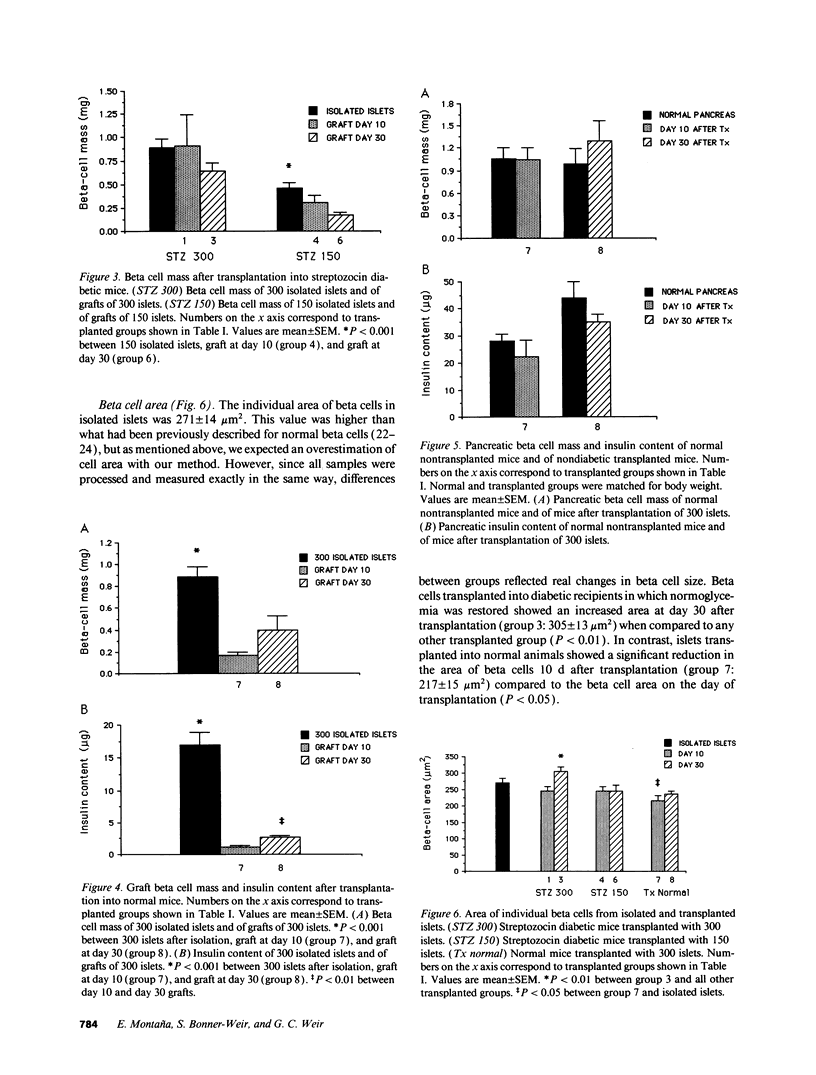
In islet transplantation, nonimmunological factors such as limited growth capacity or increased death rate could reduce the beta cell mass in the graft and lead to failure of the transplant. We studied the evolution of beta cell replication and mass after transplantation of insufficient, minimally sufficient, or excessive islet tissue. Streptozocin diabetic C57BL/6 mice received 150 or 300 syngeneic islets under the kidney capsule and normal mice received 300 islets. In streptozocin diabetic mice 300 islets restored normoglycemia; beta cell replication in transplanted islets was similar to replication in normal pancreas and beta cell mass in the graft remained constant. In contrast, 150 islets were insufficient to achieve normoglycemia; beta cell replication was increased initially but not by 18 or 30 d despite persistent hyperglycemia, and beta cell mass fell progressively. When islets were transplanted into normal recipients, beta cell replication remained normal but beta cells underwent atrophy and mass in the graft was substantially reduced. Therefore, with a successful islet transplant, in diabetic mice beta cell replication and mass remain constant. In contrast, when insufficient islet tissue is transplanted an initial increase in beta cell replication can not compensate for a decline in beta cell mass. When excessive islet tissue is transplanted, beta cell mass is reduced despite normal beta cell replication.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Maritz G., Turner R. C. A sensitive, precise radioimmunoassay of serum insulin relying on charcoal separation of bound and free hormone moieties. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Jul;70(3):487–509. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alejandro R., Cutfield R. G., Shienvold F. L., Polonsky K. S., Noel J., Olson L., Dillberger J., Miller J., Mintz D. H. Natural history of intrahepatic canine islet cell autografts. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1339–1348. doi: 10.1172/JCI112720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson A., Borg H., Hallberg A., Hellerström C., Sandler S., Schnell A. Long-term effects of cyclosporin A on cultured mouse pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1984 Jul;27 (Suppl):66–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00275649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson A., Eriksson U., Petersson B., Reibring L., Swenne I. Failure of successful intrasplenic transplantation of islets from lean mice to cure obese-hyperglycaemic mice, despite islet growth. Diabetologia. 1981 Mar;20(3):237–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00252634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson A., Korsgren O., Naeser P. DNA replication in transplanted and endogenous pancreatic islets of obese-hyperglycemic mice at different stages of the syndrome. Metabolism. 1989 Oct;38(10):974–978. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson A. The influence of hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinaemia and genetic background on the fate of intrasplenically implanted mouse islets. Diabetologia. 1983 Sep;25(3):269–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00279942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Deery D., Leahy J. L., Weir G. C. Compensatory growth of pancreatic beta-cells in adult rats after short-term glucose infusion. Diabetes. 1989 Jan;38(1):49–53. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockenbrough J. S., Weir G. C., Bonner-Weir S. Discordance of exocrine and endocrine growth after 90% pancreatectomy in rats. Diabetes. 1988 Feb;37(2):232–236. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colton C. K., Avgoustiniatos E. S. Bioengineering in development of the hybrid artificial pancreas. J Biomech Eng. 1991 May;113(2):152–170. doi: 10.1115/1.2891229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M. Ultrastructural morphometry of the pancreatic -cell. Diabetologia. 1973 Apr;9(2):115–119. doi: 10.1007/BF01230690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunger A., Korsgren O., Andersson A. DNA replication in mouse pancreatic islets transplanted subcapsularly into the kidney or intraportally into the liver. Influence of unilateral nephrectomy or partial hepatectomy. Transplantation. 1990 Apr;49(4):686–689. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199004000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith R. C., Scharp D. W., Hartman B. K., Ballinger W. F., Lacy P. E. A morphologic study of intrahepatic portal-vein islet isografts. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):201–214. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller W. F., Klempnauer J., Lück R., Steiniger B. Progressive deterioration of endocrine function after intraportal but not kidney subcapsular rat islet transplantation. Diabetes. 1991 Jan;40(1):134–140. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.1.134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkan Borg L. A., Andersson A. Long-term effects of glibenclamide on the insulin production, oxidative metabolism and quantitative ultrastructure of mouse pancreatic islets maintained in tissue culture at different glucose concentrations. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1981;18(1):65–83. doi: 10.1007/BF02056108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura T., Koffler M., Helderman J. H., Prince D., Thirlby R., Inman L., Unger R. H. Severe diabetes induced in subtotally depancreatized dogs by sustained hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 1988 May;37(5):600–609. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.5.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. B., Platt J. L., Rabe F. L., Dunn D. L., Bach F. H., Sutherland D. E. Differential roles of Mac-1+ cells, and CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in primary nonfunction and classic rejection of islet allografts. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):291–302. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp C. B., Knight M. J., Scharp D. W., Ballinger W. F., Lacy P. E. Effect of transplantation site on the results of pancreatic islet isografts in diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1973 Dec;9(6):486–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00461694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsgren O., Jansson L., Andersson A. Effects of hyperglycemia on function of isolated mouse pancreatic islets transplanted under kidney capsule. Diabetes. 1989 Apr;38(4):510–515. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsgren O., Jansson L., Sandler S., Andersson A. Hyperglycemia-induced B cell toxicity. The fate of pancreatic islets transplanted into diabetic mice is dependent on their genetic background. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):2161–2168. doi: 10.1172/JCI114955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Cooper H. E., Deal D. A., Weir G. C. Chronic hyperglycemia is associated with impaired glucose influence on insulin secretion. A study in normal rats using chronic in vivo glucose infusions. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):908–915. doi: 10.1172/JCI112389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellgren A., Schnell Landström A. H., Petersson B., Andersson A. The renal subcapsular site offers better growth conditions for transplanted mouse pancreatic islet cells than the liver or spleen. Diabetologia. 1986 Sep;29(9):670–672. doi: 10.1007/BF00869269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menger M. D., Jaeger S., Walter P., Feifel G., Hammersen F., Messmer K. Angiogenesis and hemodynamics of microvasculature of transplanted islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1989 Jan;38 (Suppl 1):199–201. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.1.s199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel P., Goetz F. C., Moudry-Munns K., Freier E., Sutherland D. E. Long-term glucose control in patients with pancreatic transplants. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Nov 1;115(9):694–699. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-9-694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reckard C. R., Barker C. F. Transplantation of isolated pancreatic islets across strong and weak histocompatibility barriers. Transplant Proc. 1973 Mar;5(1):761–763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Kahlenberg M., Healey M., Tanguay D. Cyclosporine is detrimental to islet procurement from adult pancreatic tissue. Transplant Proc. 1991 Feb;23(1 Pt 1):767–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler S., Jansson L. Blood flow measurements in autotransplanted pancreatic islets of the rat. Impairment of the blood perfusion of the graft during hyperglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):17–21. doi: 10.1172/JCI113044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Herman L. Stereological analysis of normal rabbit pancreatic islets. Am J Anat. 1981 May;161(1):71–84. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001610106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharp D. W., Lacy P. E., Santiago J. V., McCullough C. S., Weide L. G., Boyle P. J., Falqui L., Marchetti P., Ricordi C., Gingerich R. L. Results of our first nine intraportal islet allografts in type 1, insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Transplantation. 1991 Jan;51(1):76–85. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199101000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagner J. I., Samols E. The induction of capillary bed development by endothelial cell growth factor before islet transplantation may prevent islet ischemia. Transplant Proc. 1990 Apr;22(2):824–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun A. M., Coddling J. A., Haist R. E. A study of glucose tolerance and insulin response in partially depancreatized dogs. Diabetes. 1974 May;23(5):424–432. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.5.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenne I., Andersson A. Effect of genetic background on the capacity for islet cell replication in mice. Diabetologia. 1984 Oct;27(4):464–467. doi: 10.1007/BF00273912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenne I. Effects of aging on the regenerative capacity of the pancreatic B-cell of the rat. Diabetes. 1983 Jan;32(1):14–19. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenne I. The role of glucose in the in vitro regulation of cell cycle kinetics and proliferation of fetal pancreatic B-cells. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):754–760. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzakis A. G., Ricordi C., Alejandro R., Zeng Y., Fung J. J., Todo S., Demetris A. J., Mintz D. H., Starzl T. E. Pancreatic islet transplantation after upper abdominal exenteration and liver replacement. Lancet. 1990 Aug 18;336(8712):402–405. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91946-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tze W. I., Wong F. C., Tingle A. J. The use of hypaque-ficoll in the isolation of pancreatic islets in rats. Transplantation. 1976 Aug;22(2):201–205. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197608000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock G. L., Dabbs K. D., Evans M. G., Cattral M. S., Kneteman N. M., Rajotte R. V. Critical mass of islets that function after implantation in a large mammalian. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1990;25:156–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock G. L., Kneteman N. M., Ryan E., Seelis R. E., Rabinovitch A., Rajotte R. V. Normoglycaemia after transplantation of freshly isolated and cryopreserved pancreatic islets in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1991 Jan;34(1):55–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00404026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock G. L., Rajotte R. V. Critical mass of purified islets that induce normoglycemia after implantation into dogs. Diabetes. 1988 Apr;37(4):467–470. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasugi H., Mizumoto R., Sakurai H., Honjo I. Changes in carbohydrate metabolism and endocrine function of remnant pancreas after major pancreatic resection. Am J Surg. 1976 Nov;132(5):577–580. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(76)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellin A. E., Vecchione T. R., Donovan A. J. Distal pancreatectomy for pancreatic trauma. Am J Surg. 1972 Aug;124(2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(72)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deFazio A., Leary J. A., Hedley D. W., Tattersall M. H. Immunohistochemical detection of proliferating cells in vivo. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 May;35(5):571–577. doi: 10.1177/35.5.3549891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]