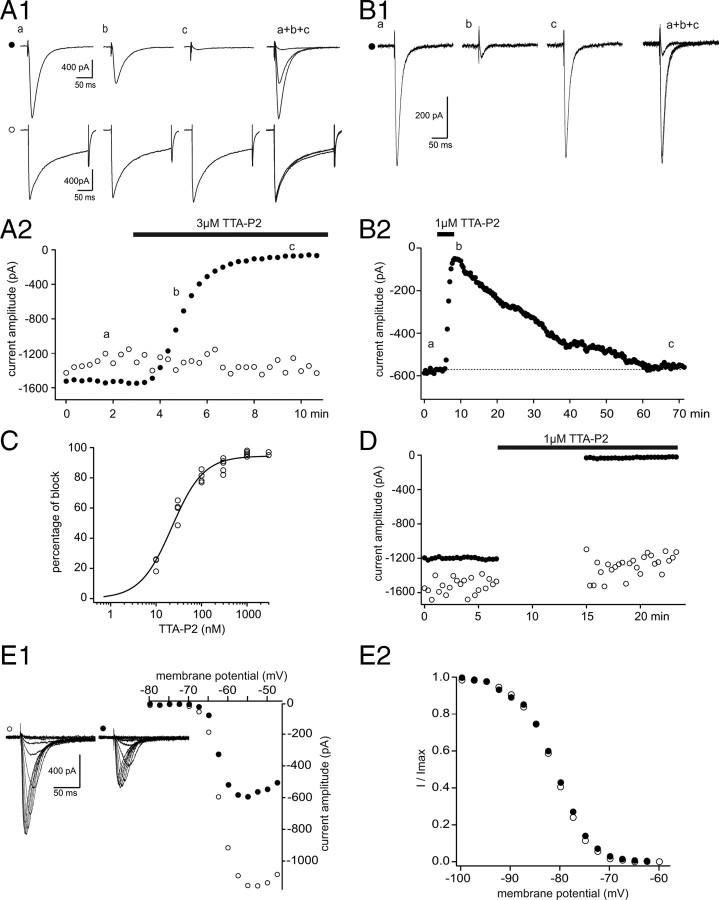
Figure 1.
TTA-P2 fully and reversibly blocks T-type Ca2+ current without affecting HVA Ca2+ currents in VB TC neurons. A, IT were evoked every 20 s by step depolarization (200 ms long) to −50 mV after a 1 s hyperpolarizing prepulse to −100 mV. HVA Ca2+ currents were similarly evoked by step depolarization to 10 mV from the −60 mV holding potential. A1, Traces illustrate IT (●, top traces) and HVA Ca2+ currents (○, bottom traces) recorded in the same VB neuron under control condition (a) and in the presence of 3 μm TTA-P2 (b, 2 min application; c, 5 min application). A2, The peak amplitude of IT (●) and HVA Ca2+ currents (○) are plotted against time. TTA-P2 produced a 95% block of IT without any effect on the HVA Ca2+ currents. B1, B2, Same protocols as in A1 and A2 in a different VB TC neuron. A full recovery of the amplitude of IT was obtained after 55 min of wash-out of 1 μm TTA-P2. C, Dose–response curve of the effect of TTA-P2 on the amplitude of IT. Data were fitted with the following equation: y = ymax/(1 + IC50/x)n, where IC50 = 22 nm, ymax = 94.5%, and n = 1.2. D, Same protocols as in A1 and A2. Interruption of the stimulating protocols during the first 8 min of 1 μm TTA-P2 application did not preclude the block of IT. E, Activation and inactivation properties of IT were estimated in the same neuron under control condition and after 20 min of 25 nm TTA-P2 application. The neuron was maintained at −60 mV between protocols. E1, I–V curves were constructed by successive step depolarizations from −80 to −45 mV (2.5 mV increments) preceded by a 1 s hyperpolarizing prepulse to −100 mV. Left traces illustrate currents evoked at the various potentials under control conditions (○) and in the presence of TTA-P2 (●). Despite the strong decrease in current amplitude induced by TTA-P2 application, the apparent voltage dependence of channel activation appears similar in control condition (○) and in the presence of TTA-P2 (●). E2, Normalized steady-state inactivation curves. Inactivation of T-type Ca2+ channels was induced using a 1 s prepulse of increasing potential (from −100 to −60 mV with 2.5 mV increments), and the resulting channel availability was estimated from the normalized current amplitude measured at −50 mV. Note the lack of any significant change in the presence of TTA-P2.