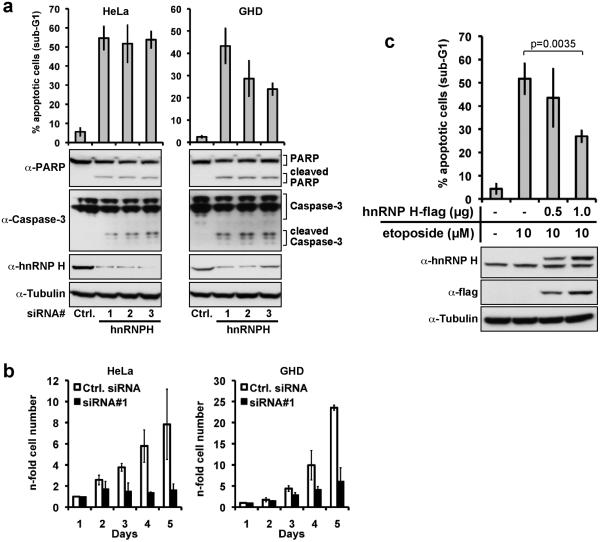
Figure 2. Knock-down of hnRNP H induces apoptosis in carcinoma cell lines.
(a) HeLa cells and GHD cells were transfected with with three different hnRNP H specific siRNA oligonucleotides (siRNA#1-3) or scrambled control siRNA (Ctrl. siRNA) at 100nM final concentration. Three days after transfection, apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry assessing fragmented DNA content (subG1) (upper panel). Additionally, cells were lysed, and expression of hnRNP H, Caspase-3, and PARP was assessed by immunoblotting (lower panels). Shown are mean values with SD from three independent experiments. (b) Numbers of HeLa and GHD-1 cells were determined in a time kinetic following siRNA#1 (black bars), or control siRNA (open bars) transfection. Results represent the mean with standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. (c) HnRNP H overexpression partly counteracts etoposide-induced apoptosis. HeLa cells were transfected with indicated amounts of a hnRNP H expression plasmid, and treated with 10μM etoposide 24 hours later. 72 hours post transfection the proportion of apoptotic cells was assessed by measuring DNA fragmentation by flow cytometry. Shown are mean values with SD from three independent experiments (upper panel). Additionally, cells were lysed, and hnRNP H- and flag- expression was assessed by immunoblotting (lower panel).